High-Fat Diet and Female Fertility
- PMID: 28586412
- PMCID: PMC6283234
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2017-00371
High-Fat Diet and Female Fertility
Abstract
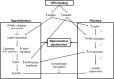
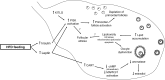
The prevalence of obesity is high among reproductive-age women and is associated with impaired reproductive function. Obesity is multifactorial in origin, yet many cases of obesity result from overconsumption of a diet high in fat. Excess dietary fat increases both adipose and nonadipose tissue lipid content and, through lipotoxicity, leads to cell dysfunction and death. High dietary fat intake, with or without the development of obesity, impairs female hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis functionality and fertility. Based on the current evidence, it appears the reproductive dysfunction involves increased leptin and insulin signaling at the various levels of the HPO axis, as well as changes in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ actions and increased inflammation, yet other mechanisms may also be involved. This review summarizes the current body of knowledge on impaired female reproductive function after high-fat diet exposure, as well as discusses proposed mechanisms through which this may occur.
Copyright © 2017 Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Flegal KM. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2011–2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2015;(219):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bellver J, Ayllón Y, Ferrando M, Melo M, Goyri E, Pellicer A, Remohí J, Meseguer M. Female obesity impairs in vitro fertilization outcome without affecting embryo quality. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(2):447–454. - PubMed
-
- Rittenberg V, Seshadri S, Sunkara SK, Sobaleva S, Oteng-Ntim E, El-Toukhy T. Effect of body mass index on IVF treatment outcome: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod Biomed Online. 2011;23(4):421–439. - PubMed
-
- Maheshwari A, Stofberg L, Bhattacharya S. Effect of overweight and obesity on assisted reproductive technology—a systematic review. Hum Reprod Update. 2007;13(5):433–444. - PubMed
-
- Turner-McGrievy GM, Grant BL. Prevalence of body mass index and body weight cut-off points for in vitro fertilization treatment at U.S. clinics and current clinic weight loss strategy recommendations. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2015;18(3):215–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

