Fetal Exposure to High Maternal Thyroid Hormone Levels Causes Central Resistance to Thyroid Hormone in Adult Humans and Mice
- PMID: 28586435
- PMCID: PMC5587072
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2017-00019
Fetal Exposure to High Maternal Thyroid Hormone Levels Causes Central Resistance to Thyroid Hormone in Adult Humans and Mice
Abstract
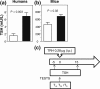
Context: Fetuses exposed to the high thyroid hormone (TH) levels of mothers with resistance to thyroid hormone beta (RTH-β), due to mutations in the THRB gene, have low birth weight and suppressed TSH.
Objective: Determine if such exposure to high TH levels in embryonic life has a long-term effect into adulthood.
Design: Observations in humans with a parallel design on animals to obtain a preliminary information regarding mechanism.
Setting: University research centers.
Patients or other participants: Humans and mice with no RTH-β exposed during intrauterine life to high TH levels from mothers who were euthyroid due to RTH-β. Controls were humans and mice of the same genotype but born to fathers with RTH-β and mothers without RTH-β and thus, with normal serum TH levels.
Interventions: TSH responses to stimulation with thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) during adult life in humans and male mice before and after treatment with triiodothyronine (T3). We also measured gene expression in anterior pituitaries, hypothalami, and cerebral cortices of mice.
Results: Adult humans and mice without RTH-β, exposed to high maternal TH in utero, showed persistent central resistance to TH, as evidenced by reduced responses of serum TSH to TRH when treated with T3. In mice, anterior pituitary TSH-β and deiodinase 3 (D3) mRNAs, but not hypothalamic and cerebral cortex D3, were increased.
Conclusions: Adult humans and mice without RTH-β exposed in utero to high maternal TH levels have persistent central resistance to TH. This is likely mediated by the increased expression of D3 in the anterior pituitary, enhancing local T3 degradation.
Copyright © 2017 Endocrine Society
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prenatal Diagnosis of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone and Its Clinical Implications.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Oct 1;102(10):3775-3782. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01251. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28938413 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal loss associated with excess thyroid hormone exposure.JAMA. 2004 Aug 11;292(6):691-5. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.6.691. JAMA. 2004. PMID: 15304465
-
Effects of maternal levels of thyroid hormone (TH) on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid set point: studies in TH receptor beta knockout mice.Endocrinology. 2007 Nov;148(11):5305-12. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0677. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17690164
-
[Syndromes of resistance to thyroid hormone and inappropriate secretion of TSH (SITSH)].Nihon Rinsho. 2012 Nov;70(11):1951-7. Nihon Rinsho. 2012. PMID: 23214067 Review. Japanese.
-
Syndrome of resistance to thyroid hormone: insights into thyroid hormone action.Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1996 Jan;211(1):49-61. doi: 10.3181/00379727-211-43951. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1996. PMID: 8594618 Review.
Cited by
-
Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Beta: A Focused Review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 31;12:656551. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.656551. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33868182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone and Its Clinical Implications.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Oct 1;102(10):3775-3782. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01251. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28938413 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychological Alterations in Patients with Congenital Hypothyroidism Treated with Levothyroxine: Linked Factors and Thyroid Hormone Hyposensitivity.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 15;11(12):3427. doi: 10.3390/jcm11123427. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35743497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene polymorphisms and thyroid hormone signaling: implication for the treatment of hypothyroidism.Endocrine. 2024 May;84(2):309-319. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03528-y. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 37740833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of T3 Availability in the Developing Brain: The Mouse Genetics Contribution.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 May 28;9:265. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00265. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29892264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glinoer D. The regulation of thyroid function in pregnancy: pathways of endocrine adaptation from physiology to pathology. Endocr Rev. 1997;18(3):404–433. - PubMed
-
- Abramson J, Stagnaro-Green A. Thyroid antibodies and fetal loss: an evolving story. Thyroid. 2001;11(1):57–63. - PubMed
-
- Refetoff S, Weiss RE, Usala SJ. The syndromes of resistance to thyroid hormone. Endocr Rev. 1993;14(3):348–399. - PubMed
-
- Anselmo J, Cao D, Karrison T, Weiss RE, Refetoff S. Fetal loss associated with excess thyroid hormone exposure. JAMA. 2004;292(6):691–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

