Presence of Human Hepegivirus-1 in a Cohort of People Who Inject Drugs
- PMID: 28586923
- PMCID: PMC5721525
- DOI: 10.7326/M17-0085
Presence of Human Hepegivirus-1 in a Cohort of People Who Inject Drugs
Abstract
Background: Next-generation metagenomic sequencing (NGMS) has opened new frontiers in microbial discovery but has been clinically characterized in only a few settings.
Objective: To explore the plasma virome of persons who inject drugs and to characterize the sensitivity and accuracy of NGMS compared with quantitative clinical standards.
Design: Longitudinal and cross-sectional studies.
Setting: A clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01285050) and a well-characterized cohort study of persons who have injected drugs.
Participants: Persons co-infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) and HIV.
Measurements: Viral nucleic acid in plasma by NGMS and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
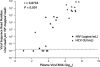
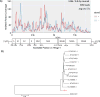
Results: Next-generation metagenomic sequencing generated a total of 600 million reads, which included the expected HIV and HCV RNA sequences. HIV and HCV reads were consistently identified only when samples contained more than 10 000 copies/mL or IU/mL, respectively, as determined by quantitative PCR. A novel RNA virus, human hepegivirus-1 (HHpgV-1), was also detected by NGMS in 4 samples from 2 persons in the clinical trial. Through use of a quantitative PCR assay for HHpgV-1, infection was also detected in 17 (10.9%) of 156 members of a cohort of persons who injected drugs. In these persons, HHpgV-1 viremia persisted for a median of at least 4538 days and was associated with detection of other bloodborne viruses, such as HCV RNA and SEN virus D.
Limitation: The medical importance of HHpgV-1 infection is unknown.
Conclusion: Although NGMS is insensitive for detection of viruses with relatively low plasma nucleic acid concentrations, it may have broad potential for discovery of new viral infections of possible medical importance, such as HHpgV-1.
Primary funding source: National Institutes of Health.
Figures
Comment in
-
Presence of Human Hepegivirus-1 in a Cohort of People Who Inject Drugs.Ann Intern Med. 2018 Jan 16;168(2):158. doi: 10.7326/L17-0525. Ann Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29335727 No abstract available.
-
Presence of Human Hepegivirus-1 in a Cohort of People Who Inject Drugs.Ann Intern Med. 2018 Jan 16;168(2):157-158. doi: 10.7326/L17-0526. Ann Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29335728 No abstract available.
-
Presence of Human Hepegivirus-1 in a Cohort of People Who Inject Drugs.Ann Intern Med. 2018 Jan 16;168(2):158-159. doi: 10.7326/L17-0527. Ann Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29335729 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rascovan N, Duraisamy R, Desnues C. Metagenomics and the Human Virome in Asymptomatic Individuals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016;70:125–41. - PubMed
-
- Adams NJ, Prescott LE, Jarvis LM, Lewis JC, McClure MO, Smith DB, et al. Detection in chimpanzees of a novel flavivirus related to GB virus-C/hepatitis G virus. J Gen Virol. 1998;79(Pt 8):1871–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
