Prostaglandin E2-Induced COX-2 Expressions via EP2 and EP4 Signaling Pathways in Human LoVo Colon Cancer Cells
- PMID: 28587064
- PMCID: PMC5485956
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18061132
Prostaglandin E2-Induced COX-2 Expressions via EP2 and EP4 Signaling Pathways in Human LoVo Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
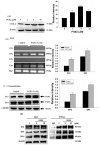
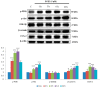
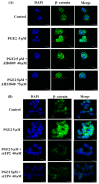
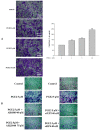
Metastasis is the most dangerous risk faced by patients with hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer (HNPCC). The expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) has been observed in several types of human cancers and regulates the efficacy of many therapies. Here, we show that treatment with various concentrations of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; 0, 1, 5 or 10 μM) promotes the migration ability of the human LoVo colon cancer cell line. As demonstrated by mRNA and protein expression analyses, EP2 and EP4 are the major PGE2 receptors expressed on the LoVo cell membrane. The Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt cell survival pathway was upregulated by EP2 and EP4 activation. Following the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, β-catenin translocated into the nucleus and triggered COX2 transcription via LEF-1 and TCF-4 and its subsequent translation. COX2 expression correlated with the elevation in the migration ability of LoVo cells. The experimental evidence shows a possible mechanism by which PGE2 induces cancer cell migration and further suggests PGE2 to be a potential therapeutic target in colon cancer metastasis. On inhibition of PGE2, in order to determine the downstream pathway, the levels of PI3K/Akt pathway were suppressed and the β-catenin expression was also modulated. Inhibition of EP2 and EP4 shows that PGE2 induces protein expression of COX-2 through EP2 and EP4 receptors in LoVo colon cancer cells.
Keywords: COX-2; EP2 and EP4 receptors; hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer (HNPCC); prostaglandin E2 (PGE2); β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

