Natural Products as Alternative Choices for P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibition
- PMID: 28587082
- PMCID: PMC6152721
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22060871
Natural Products as Alternative Choices for P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibition
Abstract
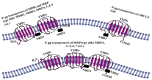
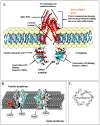
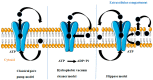
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is regarded as one of the bottlenecks of successful clinical treatment for numerous chemotherapeutic agents. Multiple key regulators are alleged to be responsible for MDR and making the treatment regimens ineffective. In this review, we discuss MDR in relation to P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and its down-regulation by natural bioactive molecules. P-gp, a unique ATP-dependent membrane transport protein, is one of those key regulators which are present in the lining of the colon, endothelial cells of the blood brain barrier (BBB), bile duct, adrenal gland, kidney tubules, small intestine, pancreatic ducts and in many other tissues like heart, lungs, spleen, skeletal muscles, etc. Due to its diverse tissue distribution, P-gp is a novel protective barrier to stop the intake of xenobiotics into the human body. Over-expression of P-gp leads to decreased intracellular accretion of many chemotherapeutic agents thus assisting in the development of MDR. Eventually, the effectiveness of these drugs is decreased. P-gp inhibitors act by altering intracellular ATP levels which are the source of energy and/or by affecting membrane contours to increase permeability. However, the use of synthetic inhibitors is known to cause serious toxicities. For this reason, the search for more potent and less toxic P-gp inhibitors of natural origin is underway. The present review aims to recapitulate the research findings on bioactive constituents of natural origin with P-gp inhibition characteristics. Natural bioactive constituents with P-gp modulating effects offer great potential for semi-synthetic modification to produce new scaffolds which could serve as valuable investigative tools to recognize the function of complex ABC transporters apart from evading the systemic toxicities shown by synthetic counterparts. Despite the many published scientific findings encompassing P-gp inhibitors, however, this article stand alones because it provides a vivid picture to the readers pertaining to Pgp inhibitors obtained from natural sources coupled with their mode of action and structures. It provides first-hand information to the scientists working in the field of drug discovery to further synthesise and discover new P-gp inhibitors with less toxicity and more efficacies.
Keywords: ABC transporters; P-glycoprotein (P-gp); P-gp inhibitors; chemotherapy; multi drug resistance (MDR); xenobiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













































Similar articles
-
β-carotene reverses multidrug resistant cancer cells by selectively modulating human P-glycoprotein function.Phytomedicine. 2016 Mar 15;23(3):316-23. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26969385
-
Marine Natural Products as Models to Circumvent Multidrug Resistance.Molecules. 2016 Jul 8;21(7):892. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070892. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27399665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural recognition of tubulysin B derivatives by multidrug resistance efflux transporters in human cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):49973-49987. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18385. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28637003 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by Marsdenia tenacissima and its main active ingredients polyoxypregnanes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 May 5;203:110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.051. Epub 2017 Mar 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28363522
-
Not only P-glycoprotein: Amplification of the ABCB1-containing chromosome region 7q21 confers multidrug resistance upon cancer cells by coordinated overexpression of an assortment of resistance-related proteins.Drug Resist Updat. 2017 May;32:23-46. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Drug Resist Updat. 2017. PMID: 29145976 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Effect of Satureja khuzestanica Essential oil on MDR1 Gene Expression in Leishmania major.Acta Parasitol. 2024 Mar;69(1):526-532. doi: 10.1007/s11686-023-00780-0. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Acta Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38227108
-
Phytol and Heptacosane Are Possible Tools to Overcome Multidrug Resistance in an In Vitro Model of Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;15(3):356. doi: 10.3390/ph15030356. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337153 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Inhibitors of P-glycoprotein in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 18;24(4):4140. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044140. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring new Horizons in overcoming P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug-resistant breast cancer via nanoscale drug delivery platforms.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Sep 6;2:100054. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100054. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictions of the Biological Effects of the Main Components of Tarragon Essential Oil.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1860. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051860. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ikegawa T., Ushigome F., Koyabu N., Morimoto S., Shoyama Y., Naito M., Tsuruo T., Ohtani H., Sawada Y. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein by orange juice components, polymethoxyflavones in adriamycin-resistant human myelogenous leukemia (K562/ADM) cells. Cancer Lett. 2000;160:21–28. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3835(00)00549-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

