NF-κB Members Left Home: NF-κB-Independent Roles in Cancer
- PMID: 28587092
- PMCID: PMC5489812
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines5020026
NF-κB Members Left Home: NF-κB-Independent Roles in Cancer
Abstract
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) has been long considered a master regulator of inflammation and immune responses. Additionally, aberrant NF-κB signaling has been linked with carcinogenesis in many types of cancer. In recent years, the study of NF-κB members in NF-κB unrelated pathways provided novel attractive targets for cancer therapy, specifically linked to particular pathologic responses. Here we review specific functions of IκB kinase complexes (IKKs) and IκBs, which have distinctly tumor promoting or suppressing activities in cancer. Understanding how these proteins are regulated in a tumor-related context will provide new opportunities for drug development.
Keywords: Cancer; IKKs; IκBs; NF-κB; Non-conventional pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
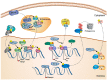
 Activation/Regulation/Phosphorylation;
Activation/Regulation/Phosphorylation;  Migration;
Migration;  Inactivation.
Inactivation.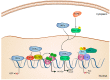
 Activation/Regulation/Phosphorylation;
Activation/Regulation/Phosphorylation;  Inactivation;
Inactivation;  Inhibition
InhibitionReferences
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

