Therapeutic Applications of Rose Hips from Different Rosa Species
- PMID: 28587101
- PMCID: PMC5485961
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18061137
Therapeutic Applications of Rose Hips from Different Rosa Species
Abstract
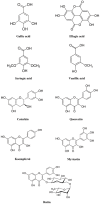
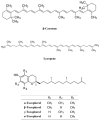
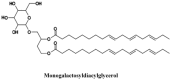
Rosa species, rose hips, are widespread wild plants that have been traditionally used as medicinal compounds for the treatment of a wide variety of diseases. The therapeutic potential of these plants is based on its antioxidant effects caused by or associated with its phytochemical composition, which includes ascorbic acid, phenolic compounds and healthy fatty acids among others. Over the last few years, medicinal interest in rose hips has increased as a consequence of recent research that has studied its potential application as a treatment for several diseases including skin disorders, hepatotoxicity, renal disturbances, diarrhoea, inflammatory disorders, arthritis, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, obesity and cancer. In this review, the role of different species of Rosa in the prevention of treatment of various disorders related to oxidative stress, is examined, focusing on new therapeutic approaches from a molecular point of view.
Keywords: Rose hip; antimicrobial; antioxidants; arthritis; cancer; diabetes; functional food; neural disorder; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of biological activities and phytochemical composition of two rose hips and their preserves: Rosa canina L. and Rosa arvensis Huds.Food Chem. 2016 Feb 1;192:907-14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.089. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 26304428
-
Phytochemical composition and in vitro functional properties of three wild rose hips and their traditional preserves.Food Chem. 2018 Feb 15;241:290-300. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.111. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 28958531
-
In vivo anti-inflammatory effect of Rosa canina L. extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):880-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.006. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21771653
-
Rosa canina - Rose hip pharmacological ingredients and molecular mechanics counteracting osteoarthritis - A systematic review.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jul;60:152958. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152958. Epub 2019 May 12. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31138475
-
A Review on the Phytochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Rosa laevigata: A Medicinal and Edible Plant.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2021;69(5):421-431. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c20-00743. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 33952852 Review.
Cited by
-
A Pilot Study of a Natural Food Supplement as New Possible Therapeutic Approach in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Jul 10;13(7):148. doi: 10.3390/ph13070148. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32664308 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic Composition of Artichoke Waste and its Antioxidant Capacity on Differentiated Caco-2 Cells.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 25;11(8):1723. doi: 10.3390/nu11081723. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31349733 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Characterization of an Ethosomal Gel Encapsulating Rosehip Extract.Gels. 2023 Apr 25;9(5):362. doi: 10.3390/gels9050362. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37232954 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Pomological and Physical Parameters in Rosehips during Ripening.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;12(6):1314. doi: 10.3390/plants12061314. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36987001 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of betulinic and ursolic acids and phenolics extraction from endemic Rosa pisiformis using Box-Behnken design in relation to cytotoxic activities.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 7;15(1):1228. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80174-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39774620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Punchard N.A., Kelly F.J. Free Radicals: A Practical Approach. IRL Press at Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources