Chronic Inflammatory Diseases and Green Tea Polyphenols
- PMID: 28587181
- PMCID: PMC5490540
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9060561
Chronic Inflammatory Diseases and Green Tea Polyphenols
Abstract
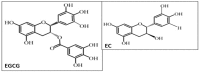
Chronic inflammatory diseases affect millions of people globally and the incidence rate is on the rise. While inflammation contributes to the tissue healing process, chronic inflammation can lead to life-long debilitation and loss of tissue function and organ failure. Chronic inflammatory diseases include hepatic, gastrointestinal and neurodegenerative complications which can lead to malignancy. Despite the millennial advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic modalities, there remains no effective cure for patients who suffer from inflammatory diseases. Therefore, patients seek alternatives and complementary agents as adjunct therapies to relieve symptoms and possibly to prevent consequences of inflammation. It is well known that green tea polyphenols (GrTPs) are potent antioxidants with important roles in regulating vital signaling pathways. These comprise transcription nuclear factor-kappa B mediated I kappa B kinase complex pathways, programmed cell death pathways like caspases and B-cell lymphoma-2 and intervention with the surge of inflammatory markers like cytokines and production ofcyclooxygenase-2. This paper concisely reviews relevant investigations regarding protective effects of GrTPs and some reported adverse effects, as well as possible applications for GrTPs in the treatment of chronic and inflammatory complications.
Keywords: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG); chronic inflammatory diseases; green tea polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oz H.S. Multiorgan chronic inflammatory hepatobiliary pancreatic murine model deficient in tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2. [(accessed on 7 June 2016)];World J. Gastroenterol. 2016 22:4988–4998. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.4988. Available online: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i21/4988.htm. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources