Cross-Kingdom Regulation of Putative miRNAs Derived from Happy Tree in Cancer Pathway: A Systems Biology Approach
- PMID: 28587194
- PMCID: PMC5486014
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18061191
Cross-Kingdom Regulation of Putative miRNAs Derived from Happy Tree in Cancer Pathway: A Systems Biology Approach
Abstract
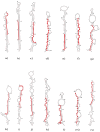
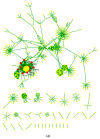
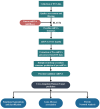
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are well-known key regulators of gene expression primarily at the post-transcriptional level. Plant-derived miRNAs may pass through the gastrointestinal tract, entering into the body fluid and regulate the expression of endogenous mRNAs. Camptotheca acuminata, a highly important medicinal plant known for its anti-cancer potential was selected to investigate cross-kingdom regulatory mechanism and involvement of miRNAs derived from this plant in cancer-associated pathways through in silico systems biology approach. In this study, total 33 highly stable putative novel miRNAs were predicted from the publically available 53,294 ESTs of C. acuminata, out of which 14 miRNAs were found to be regulating 152 target genes in human. Functional enrichment, gene-disease associations and network analysis of these target genes were carried out and the results revealed their association with prominent types of cancers like breast cancer, leukemia and lung cancer. Pathways like focal adhesion, regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes and mTOR signaling pathways were found significantly associated with the target genes. The regulatory network analysis showed the association of some important hub proteins like GSK3B, NUMB, PEG3, ITGA2 and DLG2 with cancer-associated pathways. Based on the analysis results, it can be suggested that the ingestion of the C. acuminata miRNAs may have a functional impact on tumorigenesis in a cross-kingdom way and may affect the physiological condition at genetic level. Thus, the predicted miRNAs seem to hold potentially significant role in cancer pathway regulation and therefore, may be further validated using in vivo experiments for a better insight into their mechanism of epigenetic action of miRNA.
Keywords: Camptotheca acuminata; cancer; cross-kingdom regulation; miRNA; protein-protein interaction network.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A systems biology approach for miRNA-mRNA expression patterns analysis in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2016;16(1):31-45. doi: 10.3233/CBM-150538. Cancer Biomark. 2016. PMID: 26484609
-
The Complexity of Posttranscriptional Small RNA Regulatory Networks Revealed by In Silico Analysis of Gossypium arboreum L. Leaf, Flower and Boll Small Regulatory RNAs.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 12;10(6):e0127468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127468. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26070200 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology approach identifies key regulators and the interplay between miRNAs and transcription factors for pathological cardiac hypertrophy.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:157-169. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.056. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30844478
-
MicroRNAs in trees.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;80(1):37-53. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9864-z. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22161564 Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Cancer Biology and Therapy from a Systems Biology Perspective.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1385:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08356-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36352209 Review.
Cited by
-
Employing in silico investigations to determine the cross-kingdom approach for Curcuma longa miRNAs and their human targets.Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2023;12(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s43088-022-00330-z. Epub 2023 Jan 7. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2023. PMID: 36644780 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Role of Cluster Bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) Derived miRNAs in Human and Cattle Health.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 1;15(4):448. doi: 10.3390/genes15040448. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674383 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA sequencing and identification of papaya (Carica papaya L.) miRNAs with potential cross-kingdom human gene targets.Mol Genet Genomics. 2022 Jul;297(4):981-997. doi: 10.1007/s00438-022-01904-3. Epub 2022 May 16. Mol Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35570207 Free PMC article.
-
A Timely Review of Cross-Kingdom Regulation of Plant-Derived MicroRNAs.Front Genet. 2021 May 3;12:613197. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.613197. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34012461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential target genes in Homo sapiens, by miRNA of Triticum aestivum: A cross kingdom computational approach.Noncoding RNA Res. 2022 Mar 18;7(2):89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.03.002. eCollection 2022 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022. PMID: 35387280 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

