Histological and functional assessment of the efficacy of constraint-induced movement therapy in rats following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
- PMID: 28587341
- PMCID: PMC5450637
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4371
Histological and functional assessment of the efficacy of constraint-induced movement therapy in rats following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
Abstract
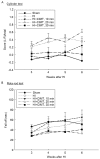
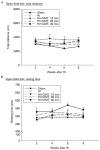
Constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT) is used in stroke rehabilitation to promote recovery of upper limb motor function. However, its efficacy in improving functional outcomes in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy has not been clearly determined in clinical or experimental research. The aim of our study was to assess the efficacy of a new experimental model of CIMT, evaluated in terms of mortality, stress, motor and cognitive function in rats having undergone a neonatal hypoxic-ischemic (HI) brain injury. Neonatal HI injury was induced at post-natal day 7 through unilateral ligation of the common carotid artery followed by exposure to hypoxia for 2 h. CIMT was implemented at 3 weeks, post-HI injury, using a pouch to constrain the unimpaired forelimb and forcing use of the affected forelimb using a motorized treadmill. After HI injury, animals demonstrated motor and cognitive deficits, as well as volumetric decreases in the ipsilateral hemisphere to arterial occlusion. CIMT yielded a modest recovery of motor and cognitive function, with no effect in reducing the size of the HI lesion or post-HI volumetric decreases in brain tissue. Therefore, although animal models of stroke have identified benefits of CIMT, CIMT was not sufficient to enhance brain tissue development and functional outcomes in an animal model of hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Based on our outcomes, we suggest that CIMT can be used as an adjunct treatment to further enhance the efficacy of a program of rehabilitation in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
Keywords: behavioral recovery; constraint-induced movement therapy; hypoxic-ischemic brain injury; neonatal rat; rehabilitation.
Figures




References
-
- Edwards AD, Brocklehurst P, Gunn AJ, Halliday H, Juszczak E, Levene M, Strohm B, Thoresen M, Whitelaw A, Azzopardi D. Neurological outcomes at 18 months of age after moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: Synthesis and meta-analysis of trial data. BMJ. 2010;340:c363. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c363. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wolf SL, Winstein CJ, Miller JP, Taub E, Uswatte G, Morris D, Giuliani C, Light KE, Nichols-Larsen D. EXCITE Investigators: Effect of constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity function 3 to 9 months after stroke: The EXCITE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2006;296:2095–2104. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.17.2095. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taub E, Miller NE, Novack TA, Cook EW, III, Fleming WC, Nepomuceno CS, Connell JS, Crago JE. Technique to improve chronic motor deficit after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74:347–354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
