Overexpression and correlation of HIF-2α, VEGFA and EphA2 in residual hepatocellular carcinoma following high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment: Implications for tumor recurrence and progression
- PMID: 28587437
- PMCID: PMC5450759
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4428
Overexpression and correlation of HIF-2α, VEGFA and EphA2 in residual hepatocellular carcinoma following high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment: Implications for tumor recurrence and progression
Abstract
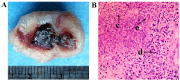
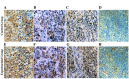
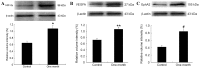
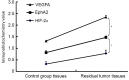
Rapid growth of residual tumors can occur as a result of their recurrence and progression. The present study aimed to investigate the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-2 subunit α (HIF-2α), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular A2 (EphA2) and angiogenesis in residual hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), following treatment with high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation, in order to investigate the association between protein expression and tumor recurrence and growth. Athymic BALB/c (nu/nu) mice were subcutaneously inoculated with the HCC cell line HepG2, in order to create xenograft tumors. Approximately 30 days post-inoculation, eight mice were treated with HIFU, whereas eight mice received no treatment and acted as the control group. Residual tumor tissues were obtained from the experimental groups after one month. Levels of HIF-2α, VEGFA, EphA2 and cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) expression was measured by immunohistochemical staining. CD31-positive vascular endothelial cells were counted to calculate microvascular density (MVD), and western blot analysis was performed to determine levels of HIF-2α, VEGFA, and EphA2 protein. It was found that the expression levels of HIF-2α, VEGFA, EphA2, and MVD proteins in residual HCC tissues were significantly higher than in the control group tissues (P<0.05). Tumor MVD was strongly correlated with VEGFA (R=0.957, P<0.01) and EphA2 (R=0.993, P<0.01) protein expression levels. Furthermore, there was a significant positive correlation between HIF-2α and EphA2 expression (R=0.991, P<0.01). The correlation between VEGFA and EphA2 expression was also positive (R=0.985, P<0.01). These data suggest that overexpression of HIF-2α, VEGFA and EphA2 is related to angiogenesis in residual HCC following HIFU ablation, potentially via their association with key mediators of recurrence.
Keywords: angiogenesis; erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular A2; hypoxia inducible factor-2 subunit α; residual hepatocellular carcinoma; vascular endothelial growth factor A.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
