Treatment of Transverse with or without Posterior Wall Fractures of Acetabulum Using a Modified Smith-Petersen Combined with Kocher-Langenbeck Approach
- PMID: 28588152
- PMCID: PMC5470865
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.901966
Treatment of Transverse with or without Posterior Wall Fractures of Acetabulum Using a Modified Smith-Petersen Combined with Kocher-Langenbeck Approach
Abstract
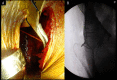
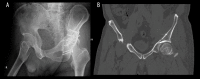
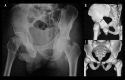
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to explore the surgical treatment of transverse with or without posterior wall fractures of the acetabulum. MATERIAL AND METHODS We surgically treated 21 consecutive cases of pure transverse (7 cases) and with posterior wall (14 cases) fractures of the acetabulum. The anterior column fractures were firstly reduced, temporarily fixed through a modified Smith-Petersen small incision, and finally fixed after the fixation of the posterior column and wall fractures, which were reduced and fixed through a Kocher-Langenbeck approach. The operative time, intra-operative blood loss, quality of reduction (Matta criteria), perioperative complications, osseous union, subsequent complications, and hip function evaluation were recorded. RESULTS The mean operative time was 198.1 min and the mean intra-operative blood loss was 938.1 ml. Anatomic reduction of the anterior column was obtained in 20 cases and was imperfect in 1 case. All posterior column and wall fractures were anatomically reduced. We followed up 18 cases for a mean duration of 16.3 (8-30) months. All the fractures achieved osseous union. The mean Harris score was 85.1 points, with an excellent result in 7 cases, good in 8, fair in 2, and poor in 1. According to modified Merle d' Aubigne and Postel score system, the results were excellent in 2 cases, good in 15, and poor in 1. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head occurred in 1 case, heterotopic ossification in 3 cases, and numbness of the anterolateral thigh in 6 cases. CONCLUSIONS For transverse with or without posterior wall fractures of the acetabulum, reduction and fixation of anterior and posterior column should be done in sequence, and a modified Smith-Petersen small incision might be a good choice in reduction and fixation of the anterior column because it possesses advantages of direct visualization and minimal invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Moed BR, Reilly MC. Acetabulum fractures. In: Rockwood CA, Bucholz RW, Court-Brown CM, et al., editors. Rockwood and Green’s fractures in adults. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. pp. 1475–83.
-
- Zhang L, Xu M, He C, et al. [Effectiveness of acetabular transverse and posterior wall fractures by Kocher-Langenbeck approach]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24:1428–31. [in Chinese] - PubMed
-
- Alexa O, Malancea RI, Puha B, et al. Results of surgical treatment of acetabular fractures using Kocher-Langenbeck approach. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2013;108:879–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

