Tunable Magneto-Optical Kerr Effects of Nanoporous Thin Films
- PMID: 28588241
- PMCID: PMC5460283
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03241-7
Tunable Magneto-Optical Kerr Effects of Nanoporous Thin Films
Abstract
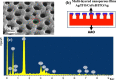
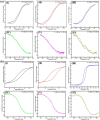
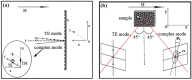
Magnetoplasmonics, combining magnetic and plasmonic functions, has attracted increasing attention owing to its unique magnetic and optical properties in various nano-architectures. In this work, Ag, CoFeB and ITO layers are fabricated on anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) porous films to form hybrid multi-layered nanoporous thin films by magnetron sputtering deposition process. The designed nanostructure supports localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and tunable magneto-optical (MO) activity, namely, the sign inversion, which can be controlled by AAO porous film geometry (pore diameter and inter-pore spacing) flexibly. The physical mechanism of this special MO phenomena is further analyzed and discussed by the correlation of Kerr rotation and electronic oscillations controlled by the surface plasmon resonance that is related to the nanoporous structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Di Pietro, P. et al. Observation of Dirac plasmons in a topological insulator. Nat Nano8, 556–560, doi:10.1038/nnano.2013.134 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Won R. View from… SMO-NP 2009: The promise of plasmonics. Nat Photon. 2009;3:500–501. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.154. - DOI
-
- Cui Y, Phang IY, Hegde RS, Lee YH, Ling XY. Plasmonic Silver Nanowire Structures for Two-Dimensional Multiple-Digit Molecular Data Storage Application. Acs Photonics. 2014;1:631–637. doi: 10.1021/ph5001154. - DOI
-
- O’Connor, D., McCurry, M., Lafferty, B. & Zayats, A. V. Plasmonic waveguide as an efficient transducer for high-density data storage. Applied Physics Letters95, doi:10.1063/1.3257701 (2009).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

