Additional molecular testing of saliva specimens improves the detection of respiratory viruses
- PMID: 28588283
- PMCID: PMC5520312
- DOI: 10.1038/emi.2017.35
Additional molecular testing of saliva specimens improves the detection of respiratory viruses
Abstract
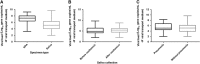
Emerging infectious diseases in humans are often caused by respiratory viruses such as pandemic or avian influenza viruses and novel coronaviruses. Microbiological testing for respiratory viruses is important for patient management, infection control and epidemiological studies. Nasopharyngeal specimens are frequently tested, but their sensitivity is suboptimal. This study evaluated the incremental benefit of testing respiratory viruses in expectorated saliva using molecular assays. A total of 258 hospitalized adult patients with suspected respiratory infections were included. Their expectorated saliva was collected without the use of any special devices. In the first cohort of 159 patients whose nasopharyngeal aspirates (NPAs) tested positive for respiratory viruses during routine testing, the viral load was measured using quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Seventeen percent of the patients (27/159) had higher viral loads in the saliva than in the NPA. The second cohort consisted of 99 patients whose NPAs tested negative for respiratory viruses using a direct immunofluorescence assay. Their NPA and saliva specimens were additionally tested using multiplex PCR. In these patients, the concordance rate by multiplex PCR between NPA and saliva was 83.8%. Multiplex PCR detected viruses in saliva samples from 16 patients, of which nine (56.3%) had at least one virus that was not detected in the NPA. Decisions on antiviral or isolation precautions would be affected by salivary testing in six patients. Although NPAs have high viral loads and remain the specimen of choice for most patients with respiratory virus infections, supplementary molecular testing of saliva can improve the clinical management of these patients.
Figures

Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2: What can saliva tell us?Oral Dis. 2021 Apr;27 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):746-747. doi: 10.1111/odi.13365. Epub 2020 May 11. Oral Dis. 2021. PMID: 32311181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Luyt CE, Brechot N, Chastre J. What role do viruses play in nosocomial pneumonia? Curr Opin Infect Dis 2014; 27: 194–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
