Behavioral Effects of a Novel Benzofuranyl-Piperazine Serotonin-2C Receptor Agonist Suggest a Potential Therapeutic Application in the Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- PMID: 28588509
- PMCID: PMC5438973
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00089
Behavioral Effects of a Novel Benzofuranyl-Piperazine Serotonin-2C Receptor Agonist Suggest a Potential Therapeutic Application in the Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Abstract
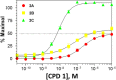
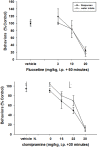
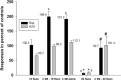
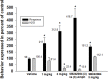
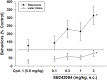
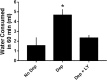
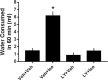
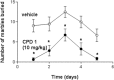
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the only effective pharmacological treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Nonetheless, their generally limited efficacy, side-effects, and delayed onset of action require improved medications for this highly prevalent disorder. Preclinical and clinical findings have suggested serotonin2C (5-HT2C) receptors as a potential drug target. Data in rats and mice are presented here on the effects of a novel 5-HT2C receptor agonist ((3S)-3-Methyl-1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-benzofuranyl]-piperazine) (CPD 1) with high potency and full efficacy at 5-HT2C receptors and less potency and partial agonism at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors. Effects of CPD 1 on consummatory (schedule-induced polydipsia in rats) and non-consummatory behaviors (marble-burying and nestlet-shredding in mice) that are repetitive and non-habituating were studied. We also evaluated the effects of CPD 1 in rats with isoproterenol- and deprivation-induced drinking in rats to compare with the polydipsia studies. The SSRIs, fluoxetine, and chlomipramine decreased the high rates of drinking in rats engendered by a schedule of intermittent food delivery (schedule-induced polydipsia). The effects of fluoxetine, but not of d-amphetamine, were prevented by the selective 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB242084. The 5-HT2C receptor agonists Ro 60-0175 and CPD 1 also decreased drinking, but unlike the SSRIs and Ro 60-0175, CPD 1 dose-dependently decreased excessive drinking without affecting lever press responses that produced food. The effects of CPD 1 were prevented by SB242084. CPD 1 also suppressed drinking induced by isoproterenol and by water deprivation without affecting normative drinking behavior. CPD 1, like fluoxetine, also suppressed marble-burying and nestlet-shredding in mice at doses that did not affect rotarod performance or locomotor activity. The behavioral specificity of effects of CPD 1 against repetitive and excessive behaviors suggests a potential therapeutic application in OCD.
Keywords: 5-HT2C receptors; Ro 60-0175; SB242084; fluoxetine; marble-burying; obsessive–compulsive disorder; schedule-induced polydipsia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of specific serotonin receptor modulation on restricted repetitive behaviors.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Dec 23;16:1078983. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1078983. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36620862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreases in nestlet shredding of mice by serotonin uptake inhibitors: comparison with marble burying.Life Sci. 2006 Mar 20;78(17):1933-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.08.002. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16182315
-
5-HT2C receptor agonists: pharmacological characteristics and therapeutic potential.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Aug;286(2):913-24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9694950
-
Activation of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors inhibits high compulsive drinking on schedule-induced polydipsia.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Feb;232(4):683-97. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3699-7. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25155310
-
Hallucinogens, serotonin and obsessive-compulsive disorder.J Psychoactive Drugs. 1998 Oct-Dec;30(4):359-66. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1998.10399711. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1998. PMID: 9924841 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Neurobiological Markers in Phenotype-stratified Rats Modeling High or Low Vulnerability to Compulsive Behavior: A Narrative Review.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(9):1924-1933. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666221121091454. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36411566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of specific serotonin receptor modulation on restricted repetitive behaviors.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Dec 23;16:1078983. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1078983. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36620862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis, Homeostatic Satiety, and Compulsions: What Can We Learn From Polydipsia?Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Aug 1;13:170. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00170. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31417376 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Fear Memory and Glutamatergic Modulation in Compulsive Drinker Rats Selected by Schedule-Induced Polydipsia.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 May 7;13:100. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00100. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31133835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pigott TA, Seay S. Biological treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Literature review. In: Swinson RP, Antony MM, Rachman S, Richter MA, editors. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Theory, Research, and Treatment. New York: Guilford Press; (1998). p. 298–326.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

