Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue: A Key Tissue Inside the Mucosal Immune System of Hens Immunized with Escherichia coli F4
- PMID: 28588575
- PMCID: PMC5438980
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00568
Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue: A Key Tissue Inside the Mucosal Immune System of Hens Immunized with Escherichia coli F4
Abstract
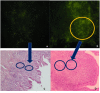
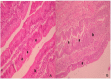
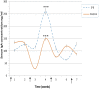
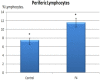
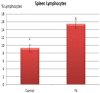
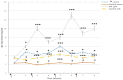
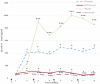
Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) is the predominant antibody found in hen's (Gallus domesticus) egg yolk. This antibody, developed against several microorganisms in hen egg yolk, has been successfully used as an alternative to immunoglobulins from mammals for use in immunodiagnostics and immunotherapy. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (E.coli) F4 is the main etiological agent associated with swine neonatal diarrhea, and it causes notable economic losses in swine production. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the relationship between humoral immune response and the activation of gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) in laying hens intramuscularly immunized with E. coli F4. Adult laying Shaver hens were immunized with a bacterin based on an inactivated lysate E. coli F4 strain that was originally isolated from neonatal piglet diarrhea, following a recommended schedule. The percentage of B lymphocytes in blood and spleen homogenates was determined by flow cytometry. Villi histomorphometry and the size of germinal centers (GC) activated in GALT and the spleen were measured in histological samples either stained with hematoxylin/eosin or through immunofluorescence. Antibody and isotype-specific antibodies in serum and egg yolk were measured using indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Secretory and serum immunoglobulin A (IgA) were measured by ELISA tests. Laying hen with intramuscular immunization with E. coli F4 lysate, activated both mucosal and systemic protection. Mucosal protection was provided through B lymphocytes, and most of them were activated on Peyer's patches and esophageal tonsils, in GALT. Furthermore, increased B lymphocyte number in the lamina propria of the gut, and increased intraepithelial plasmatic cell number, produced high levels of mucosal IgA. Activated B lymphocytes interacted with absorptive cells, immune cells, and microbiota in the gut, producing signals that were translated into a powerful physical defense by producing a greater volume of mucin from an increased number of goblet cells. Systemic protection was provided through B lymphocyte activation of spleen GC, which produced hugely specific IgY serum levels. One week later, this specific IgY was deposited in the yolk. This suggests that GALT is a key immunologic tissue inside the mucosal immune system, acting as the "command center" for humoral reaction.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; Escherichia coli F4; flow cytometry; gut-associated lymphatic tissue; hen; histomorphometry; immunoglobulin A; immunoglobulin Y technology.
Figures
References
-
- Peralta MF, Danelli MGM, Vivas AB. Rediscovering the importance of mucosal immune system (MIS) in poultry. Acad J Biotechnol (2016) 4(3):91–5.10.15413/ajb.2015.0238 - DOI
-
- Romero P, Magnoli A, Peralta MF. Biotecnología de la Inmunoglobulina Y (IgY) en animales domésticos como preventivo ó terapéutico en enfermedades entéricas. Redvet (2013) 15(1):1–8.
-
- Barman N, Nath A, Kalita N. Reflection of serum immunoglobulin isotypes in the egg yolk of laying hens immunized with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vet World (2014) 7(9):749–53.10.14202/vetworld.2014.749-753 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

