The Significant Pathways and Genes Underlying the Colon Cancer Treatment by the Traditional Chinese Medicine PHY906
- PMID: 28588641
- PMCID: PMC5447272
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8753815
The Significant Pathways and Genes Underlying the Colon Cancer Treatment by the Traditional Chinese Medicine PHY906
Abstract
Background: We attempted to explore the molecular mechanism underlying PHY906 intervention of colon cancer.
Methods: The microarray data of tumors treated by PHY906 and PBS alone were downloaded from the public Gene Expression Omnibus database. The dataset was further analyzed for the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and their related biological functions were analyzed, followed by function and pathways. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed and the significant nodes were screened by network centralities and then the significant modules analysis. Besides, they were clustered and transcriptional factors (TFs) were predicted.
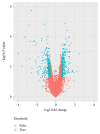
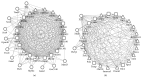
Results: The gene expression patterns changed induced by PHY906 treatment, including 414 upregulated and 337 downregulated DEGs. The biological process of response to steroid hormone stimulus and regulation of interferon-gamma production were significantly enriched by DEGs. Ezh2 (enhancer of zeste 2) was found to be the key node in PPI network. There are 12 significant TFs predicted for module 1 genes and 3 TFs for module 2 genes.
Conclusions: PHY906 treatment may function in protecting the epithelial barrier against tumor cell invasion by modulating IFN-γ level and mediating cancer cell death by activating the response to steroid hormone stimulus and activating the response to steroid hormone stimulus. E2f1, Hsfy2, and Nfyb may be therapeutic targets for colon cancer. PHY906 showed treatment efficacy in modulating cell apoptosis by intervening interferon-gamma production and response to steroid hormone stimulus. Ezh2 and its TFs such as E2f1, Hsfy2, and Nfyb may be the potential therapeutic targets for anticancer agents development.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

