Synergistic cytotoxic effects of a combined treatment of a Pinellia pedatisecta lipid-soluble extract and cisplatin on human cervical carcinoma in vivo
- PMID: 28588727
- PMCID: PMC5452894
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6091
Synergistic cytotoxic effects of a combined treatment of a Pinellia pedatisecta lipid-soluble extract and cisplatin on human cervical carcinoma in vivo
Abstract
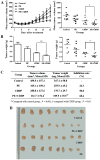
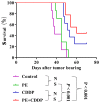
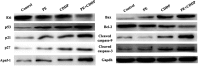
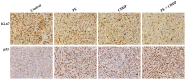
Herbal medicines are known to have numerous benefits, including lower toxicity and fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapeutic drugs. In traditional Chinese medicine, the rhizome of Pinellia pedatisecta (PE) Schott has long been used to treat cancer, undiagnosed swelling and erythema toxicum. However, its medical benefits lack support from scientific evidence. A novel lipid-soluble extract from PE has been previously verified to enhance the cytotoxicity of cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum-II (CDDP) against human cervical cancer cells in vitro. The present study evaluated the synergistic cytotoxic effects of PE and CDDP against human cervical cancer. Combination therapy of PE with CDDP exhibited synergistic cytotoxicity towards CaSki cell growth in mouse xenograft tumors. PE exhibited a cytotoxic effect on tumor size and weight, although the inhibitory ratio of tumor weight was only 26.3% in the PE-treated group. However, when mice were co-treated with PE and CDDP, the inhibitory ratio was higher than that of mice treated with CDDP alone (50.8 vs. 68.4%, respectively). The potential synergistic mechanism was likely via inhibiting the signaling E6/p53 pathway, restoring p53 function and inducing downstream tumor suppressor chain effects on apoptosis. Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry indicated thatE6protein expression was significantly decreased upon treatment with combined PE and CDDP. The expression of p53 was increased in the combined PE and CDDP treatment group. Upregulation of p53-dependent apoptosis-associated proteins, including Bcl-2-associated X protein and cleaved caspases-9 and -3, was observed in the combined PE and CDDP treatment group. Our results present a molecular basis for the future application of the combination of PE and CDDP in the treatment of cervical cancer as a novel and pharmacologically safe chemotherapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Pinelliapedatisecta Schott; cervical cancer; cisplatin; cytotoxicity; synergistic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of a novel lipid-soluble extract from Pinellia pedatisecta Schott and cisplatin on human cervical carcinoma cell lines through the regulation of DNA damage response signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2017 Apr;13(4):2121-2128. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5738. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28454371 Free PMC article.
-
Combining cisplatin with Pinellia pedatisecta Schott lipid-soluble extract induces tumor immunogenic cell death in cervical cancer.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155504. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155504. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38452404
-
A lipid-soluble extract of Pinellia pedatisecta Schott enhances antitumor T cell responses by restoring tumor-associated dendritic cell activation and maturation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;241:111980. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111980. Epub 2019 May 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31146000
-
A lipid-soluble extract of Pinellia pedatisecta Schott orchestrates intratumoral dendritic cell-driven immune activation through SOCS1 signaling in cervical cancer.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:112837. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112837. Epub 2020 Apr 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32276009
-
Immune modulation of a lipid-soluble extract of Pinellia pedatisecta Schott in the tumor microenvironment of an HPV+ tumor-burdened mouse model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 28;225:103-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.037. Epub 2018 May 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29783020
Cited by
-
Adjunctive Chinese Herbal Medicine Treatment is Associated With an Improved Survival Rate in Patients With Cervical Cancer in Taiwan: A Matched Cohort Study.Integr Cancer Ther. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15347354211061752. doi: 10.1177/15347354211061752. Integr Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34923874 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Designing and Developing Vaccines, Drugs and Therapeutic Approaches to Counter Human Papilloma Virus.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 12;9:2478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02478. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30483247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DiSilvestro PA, Ali S, Craighead PS, Lucci JA, Lee YC, Cohn DE, Spirtos NM, Tewari KS, Muller C, Gajewski WH, et al. Phase III randomized trial of weekly cisplatin and irradiation versus cisplatin and tirapazamine and irradiation in stages IB2, IIA, IIB, IIIB, and IVA cervical carcinoma limited to the pelvis: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:458–464. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.4265. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedlander M, Grogan M. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force: Guidelines for the treatment of recurrent and metastatic cervical cancer. Oncologist. 2002;7:342–347. - PubMed
-
- Travis LB, Fossa SD, Sesso HD, Frisina RD, Herrmann DN, Beard CJ, Feldman DR, Pagliaro LC, Miller RC, Vaughn DJ, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity and ototoxicity: New paradigms for translational genomics. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:pii: dju044. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen SJ, Kuo CC, Pan HY, Tsou TC, Yeh SC, Chang JY. Mechanistic basis of a combination D-penicillamine and platinum drugs synergistically inhibits tumor growth in oxaliplatin-resistant human cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmaco. 2015;l95:28–37. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.03.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
