Antifatigue Effect of Luteolin-6-C-Neohesperidoside on Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Forced Swimming of Rats through Modulation of Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 28588747
- PMCID: PMC5447270
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3159358
Antifatigue Effect of Luteolin-6-C-Neohesperidoside on Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Forced Swimming of Rats through Modulation of Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathways
Abstract
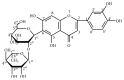
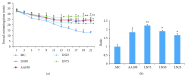
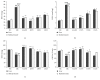
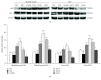
Luteolin-6-C-neohesperidoside (LN) is a flavonoid isolated from moso bamboo leaf. This study was performed to evaluate the antifatigue effect of LN on a rat model undergoing the weight-loaded forced swimming test (FST). Briefly, male Sprague-Dawley rats (20-22 weeks old) were forced to undertake exhaustive swimming every other day for 3 weeks. Each swimming session was followed by the administration of distilled water, LN (25-75 mg/kg), or ascorbic acid (100 mg/kg) 1 h later. Oral administration of LN significantly improved exercise endurance; normalized alterations in energy metabolic markers; and decreased serum lactic acid, lactate dehydrogenase, and blood urea nitrogen levels of rats that underwent FST. Moreover, LN enhanced the activities of antioxidant enzymes and antioxidant capacity, as measured by enzyme activity assays, RT-PCR, and Western blotting, as well as decreasing the levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and IL-6 and increasing the level of anti-inflammatory (IL-10) in the liver and skeletal muscle. These results suggested that LN reduces both physical and mental effects of chronic fatigue, probably by attenuating oxidative stress injury and inflammatory responses in the liver and skeletal muscle. This study thus supports the use of LN in functional foods for antifatigue and antioxidant effects.
Figures



References
-
- Son C. G. Review of the prevalence of chronic fatigue worldwide. Korean Orient Medical. 2012;33:25–33.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

