Survival of patients with lung cancer and diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 28588788
- PMCID: PMC5451856
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1224
Survival of patients with lung cancer and diabetes mellitus
Abstract
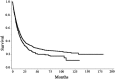
Diabetes mellitus (DM) and lung cancer are two highly globally prevalent diseases. The current study aimed to determine the prognostic significance of DM comorbidity in patients with lung cancer. All patients diagnosed at Tsukuba Medical Center Hospital and Mito Medical Center, (University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan) between April 1999 and March 2012 were followed up to 2015 and were retrospectively analyzed. DM was defined as a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level ≥126 mg/dl, a non-FPG level ≥200 mg/dl, or a hemoglobin (Hb) A1c level ≥6.5%. Additionally, patients taking medication for diabetes and those with a history of using such medications were also classified as having DM. During the study period, 1,798 patients with lung cancer were diagnosed. Within this cohort, 338 (18.8%) were classed as having lung cancer and DM. In univariate and multivariate analyses, smoking status, poorer performance status, small cell lung cancer pathology, metastatic disease and supportive care were the only unfavorable prognostic factors (all P=0.001). Additionally, multivariate analysis revealed that existing DM was an unfavorable disease-modifying factor (P=0.03612). Therefore, DM comorbidity adversely affects lung cancer outcomes. To provide prolonged quality of survival, appropriate pre-evaluation of lung cancer, as well as the patient's medical condition, including DM, is required.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; lung cancer; survival.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous