Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide regulates ephrin/Eph signalling in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts
- PMID: 28590061
- PMCID: PMC5600103
- DOI: 10.1111/jre.12463
Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide regulates ephrin/Eph signalling in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts
Abstract
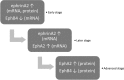
Objective: EphrinA2-EphA2 and ephrinB2-EphB4 critically engage in bidirectional signalling to modulate alveolar bone remodelling. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) derived from Porphyromonas gingivalis on ephrin/Eph signalling in periodontal ligament fibroblasts (PDLFs).
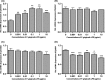
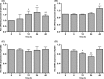
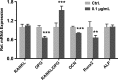
Material and methods: The primary cultured PDLFs were incubated in the absence (as a control) or presence of P. gingivalisLPS at 0.001-10 μg/mL for 24 hours. The PDLFs were then stimulated with P. gingivalisLPS at the optimal concentration (0.1 μg/mL) for different periods (6-48 hours). The expression of ephrinA2, ephrinB2, EphA2 and EphB4 was assessed by quantitative reverse-transcription real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. The osteoblastic markers alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin and Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), and the osteoclastogenesis-related factors receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin were also evaluated.
Results: The ephrinA2 and EphA2 expression was upregulated and EphB4 expression was downregulated by stimulation of P. gingivalisLPS. EphrinA2 mRNA expression in the PDLFs was significantly upregulated from 12 to 48 hours (P<.05), whereas EphA2 exhibited no change for the first 24 hours, after which there was a significant increase at 48 hours (P<.05). EphB4 exhibited lower mRNA expression at 12 and 24 hours than did the control (P<.05), but the change was insignificant at 48 hours. In contrast, the expression of ephrinB2 remained unchanged. The expressions of ephrinA2, EphA2, ephrinB2 and EphB4 at the protein level showed a similar pattern to that at the mRNA level. The expression of Runx2 and osteocalcin significantly decreased, whereas that of RANKL/osteoprotegerin increased.
Conclusion: The present study suggest that P. gingivalisLPS would contribute to a dysregulation of bone remodelling, whereby ephrinA2/EphA2 expression is stimulated and EphB4 expression is inhibited.
Keywords: ephrin/Eph; lipopolysaccharide; periodontal ligament fibroblasts.
© 2017 The Authors Journal of Periodontal Research Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Wada N, Maeda H, Tanabe K, et al. Periodontal ligament cells secrete the factor that inhibits osteoclastic differentiation and function: the factor is osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor. J Periodontal Res. 2001;36:56‐63. - PubMed
-
- Lian JB, Stein GS. Runx2/Cbfa1: a multifunctional regulator of bone formation. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:2677‐2685. - PubMed
-
- Sokos D, Everts V, de Vries TJ. Role of periodontal ligament fibroblasts in osteoclastogenesis: a review. J Periodontal Res. 2015;50:152‐159. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

