Depigmenting Effect of Resveratrol Is Dependent on FOXO3a Activation without SIRT1 Activation
- PMID: 28590410
- PMCID: PMC5486036
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18061213
Depigmenting Effect of Resveratrol Is Dependent on FOXO3a Activation without SIRT1 Activation
Abstract
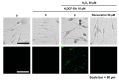
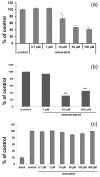
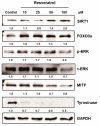
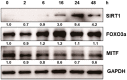
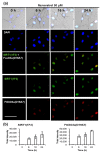
Resveratrol exhibits not only anti-melanogenic property by inhibiting microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), but also anti-aging property by activating sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). In this study, the relationship between depigmenting effect of resveratrol and SIRT1/forkhead box O (FOXO) 3a activation and was investigated. Resveratrol suppressed melanogenesis by the downregulation of MITF and tyrosinase via ERK pathway. Results showed that the expression of both SIRT1 and FOXO3a were increased. It is reported that SIRT1 is critical regulator of FOXO-mediated transcription in response to oxidative stress. However in our study, FOXO3a activation appeared earlier than that of SIRT1. Furthermore, the effect of resveratrol on the levels of MITF and tyrosinase was suppressed when melanocytes were pre-treated with SP600125 (JNK inhibitor). However, pre-treatment with SIRT1 inhibitor (EX527, or sirtinol) did not affect the levels of MITF and tyrosinase. Therefore, resveratrol inhibits melanogenesis through the activation of FOXO3a but not by the activation of SIRT1. Although SIRT1 activation by resveratrol is a well-known mechanism of resveratrol-induced antiaging effects, our study showed that not SIRT1 but FOXO3a activation is involved in depigmenting effects of resveratrol.
Keywords: extracellular signal-regulate kinase; forkhead box O; melanogenesis; resveratrol; sirtuin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resveratrol ameliorates hyperglycemia-induced renal tubular oxidative stress damage via modulating the SIRT1/FOXO3a pathway.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017 Apr;126:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 18. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28258028
-
Regulation of FOXOs and p53 by SIRT1 modulators under oxidative stress.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 11;8(9):e73875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073875. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040102 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating RUNX2 gene expression via the SIRT1/FOXO3A axis.J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Oct;26(10):2552-63. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.460. J Bone Miner Res. 2011. PMID: 21713995
-
Resveratrol as a gene regulator in the vasculature.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(4):401-8. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666140711114450. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25022271 Review.
-
Effects of Resveratrol and other Polyphenols on Sirt1: Relevance to Brain Function During Aging.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;16(2):126-136. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170703113212. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28676015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Skin Lightening Efficacy of Resveratrol and Its Analogs: From in Vitro Studies to Cosmetic Applications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 22;8(9):332. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090332. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31443469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective mechanisms of ε-viniferin in a rotenone-induced cell model of Parkinson's disease: significance of SIRT3-mediated FOXO3 deacetylation.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Nov;15(11):2143-2153. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.282264. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 32394973 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of anti-human melanoma and anti-aging mechanisms of compounds from green seaweed Caulerpa racemosa.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 11;14(1):27534. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78464-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39528552 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Resveratrol in Regulating Cutaneous Functions.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Apr 14;2020:2416837. doi: 10.1155/2020/2416837. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32382280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol improves lipid profile and recovers heart function in postoperative CABG patients.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05351-7. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40676400
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

