Genetic moderation of cocaine subjective effects by variation in the TPH1, TPH2, and SLC6A4 serotonin genes
- PMID: 28590957
- PMCID: PMC5572746
- DOI: 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000178
Genetic moderation of cocaine subjective effects by variation in the TPH1, TPH2, and SLC6A4 serotonin genes
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated variants of tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH)1, TPH2, and SLC6A4 in the moderation of the subjective effects of cocaine.
Methods: Non-treatment-seeking cocaine-dependent individuals (N=66) were intravenously administered saline and cocaine (40 mg) in a randomized order. Participants self-reported subjective effects of cocaine using a visual analog scale starting before administration of saline or cocaine (-15 min) to up to 20 min after infusion. Self-report ratings on the visual analog scale ranged from 0 (no effect) to 100 (greatest effect). Participants were genotyped for the TPH1 rs1799913, TPH2 rs4290270, and SLC6A4 5-HTTLPR variants. Repeated-measures analysis of covariance was used to examine changes in subjective effect scores over time while controlling for population structure.
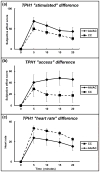
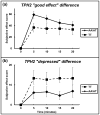
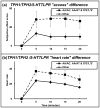
Results: Participants carrying the TPH1 rs1799913 A allele reported greater subjective response to cocaine for 'stimulated' and 'access' relative to the CC genotype group. Those carrying the TPH2 rs4290270 A allele reported higher 'good effect' and lower 'depressed' effect relative to the TT genotype group. Those carrying the SLC6A4 5-HTTLPR S' allele reported greater 'desire' and 'access' compared with the L'L' genotype group.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that TPH1, TPH2, and SLC6A4 variants moderate the subjective effects of cocaine in non-treatment-seeking cocaine-dependent participants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Methylation of the serotonin transporter gene moderates the depressive subjective effect of cocaine.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 10;418:113675. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113675. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34798166 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying the role of serotonergic 5-HTTLPR and TPH2 variants on disulfiram treatment of cocaine addiction: a preliminary study.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Nov;11(8):1001-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00839.x. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22925276 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genetic variation of the dopamine transporter (DAT1) influences the acute subjective responses to cocaine in volunteers with cocaine use disorders.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2015 Jun;25(6):296-304. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000137. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25850966 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous analysis of serotonin transporter, tryptophan hydroxylase 1 and 2 gene expression in the ventral prefrontal cortex of suicide victims.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010 Jun 5;153B(4):909-18. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31059. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010. PMID: 20052688
-
Analysis of variations in the tryptophan hydroxylase-2 (TPH2) gene in cocaine dependence.Addict Biol. 2006 Mar;11(1):76-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2006.00005.x. Addict Biol. 2006. PMID: 16759340
Cited by
-
Association of Functional Polymorphism in TPH2 Gene with Alcohol Dependence and Personality Traits: Study in Cloninger's Type I and Type II Alcohol-Dependent Inpatients.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 4;14(2):413. doi: 10.3390/genes14020413. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833340 Free PMC article.
-
TPH-2 Gene Polymorphism in Major Depressive Disorder Patients With Early-Wakening Symptom.Front Neurosci. 2018 Nov 15;12:827. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00827. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30519155 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Serotonin Transporter (SERT) Polymorphisms with Opioid Dependence and Dimensional Aspects of Cocaine Use in a Caucasian Cohort of Opioid Users.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Feb 25;17:659-670. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S286536. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 33658787 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of the serotonin transporter gene moderates the depressive subjective effect of cocaine.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 10;418:113675. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113675. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34798166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistic Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000.
-
- Brewer A, Nielsen DA, Spellicy CJ, Hamon SC, Gingrich J, Thompson-Lake DGY, Nielsen EM, Mahoney JJ, Kosten TR, Newton TF, De La Garza R. Genetic variation of the dopamine transporter (DAT1) influences the acute subjective responses to cocaine in volunteers with cocaine use disorders. Pharmacogenetics and genomics. 2015;25:296–304. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen . Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Erlbaum; Hillsdale, NJ: 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

