Necrotizing fasciitis-A catastrophic complication following routine tibia fracture surgery: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 28591027
- PMCID: PMC5466205
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006908
Necrotizing fasciitis-A catastrophic complication following routine tibia fracture surgery: A case report and literature review
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Necrotizing fasciitis-A catastrophic complication following routine tibia fracture surgery: A case report and literature review: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun 23;96(25):e7360. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007360. eCollection 2017 Jun. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 31305685 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Rationale: Necrotizing fasciitis (NF) is defined as a rare, life-threatening, rapidly spreading soft tissue infection resulting from a polymicrobial origin, with a predominance of anaerobic organisms that presents with necrosis of the muscle, fascia, and surrounding soft tissue.
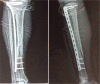
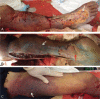
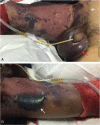
Patient concerns and diagnoses: A 64-year-old male who sustained tibia fracture caused by falling from a height underwent a tibia surgery with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique in another institution. Postoperatively, the patient had development of a very uncommon NF at the site of the tibia procedure. When the patient was transferred to our unit, he rapidly processed to toxic shock and coagulopathy.
Interventions and outcomes: Although the patient underwent antibiotics treatment in the emergency room and was transferred to the operating room for surgery promptly, the patient's condition deteriorated rapidly and he died of septic shock and multiple organ failure unfortunately.
Lessons: Our study aims to highlight the risk of NF in the elderly with diabetes during the perioperative period even if the injury is a simple closed fracture. Physicians must be vigilant to early inflammatory signs and pain in immunosuppressed patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Necrotizing fasciitis: apropos of a case].G Chir. 1997 Nov-Dec;18(11-12):797-800. G Chir. 1997. PMID: 9534330 Italian.
-
[Postoperative necrotizing fasciitis: a rare and fatal complication].Pan Afr Med J. 2016 Mar 24;23:123. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.23.123.8734. eCollection 2016. Pan Afr Med J. 2016. PMID: 27279950 Free PMC article. French.
-
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for open fractures of the proximal tibia.Clin Orthop Surg. 2012 Dec;4(4):313-20. doi: 10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.313. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012. PMID: 23205242 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumococcal necrotizing fasciitis in a patient with Type 2 diabetes.Diabet Med. 2003 Nov;20(11):899-903. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00984.x. Diabet Med. 2003. PMID: 14632714 Review.
-
Periocular necrotizing fasciitis: a review of five cases.Ophthalmology. 1997 Nov;104(11):1857-62. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(97)30016-5. Ophthalmology. 1997. PMID: 9373117 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent soft tissue inflammation, necrotizing fascitis or Sweet syndrome, diagnostic dilemma.Clin Case Rep. 2019 Nov 13;7(12):2483-2487. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2445. eCollection 2019 Dec. Clin Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31893084 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: Necrotizing fasciitis-A catastrophic complication following routine tibia fracture surgery: A case report and literature review: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun 23;96(25):e7360. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007360. eCollection 2017 Jun. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 31305685 Free PMC article.
-
A successful process of treatment with necrotizing fasciitis of upper extremities in patients with diabetes mellitus: a case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Apr 11;85(5):1947-1951. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000463. eCollection 2023 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37228965 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection and Fatal Clostridium septicum Septicemia in Myelodysplastic Syndrome: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review.Cureus. 2025 May 23;17(5):e84715. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84715. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40551931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joseph M Bellapianta, Karin Ljungquist, Ellis Tobin, et al. Necrotizing fasciitis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2009;17:174–82. - PubMed
-
- Chin-Ho W, Yi-Shi W. The diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2005;18:101–6. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen TJ, Green SD, Childers BJ. Massive soft-tissue injury: diagnosis and management of necrotizing fasciitis and purpura fulminans. Plast Reconstr Surg 2001;107:1025–35. - PubMed
-
- Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, et al. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciits) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med 2004;32:1535–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

