Surgical performance of large loop excision of the transformation zone in a training model: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 28591034
- PMCID: PMC5466212
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007026
Surgical performance of large loop excision of the transformation zone in a training model: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
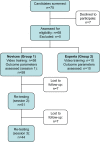
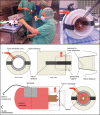
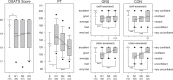
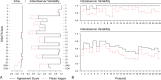
Large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) is one of the most common procedures in operative gynecology and it is a routine part of the surgical training program of residents. There is, however, no established and standardized method of teaching residents how to perform LLETZ. Here, we present a surgical training model and assessed the improvement of surgical skills during repeated hands-on trainings of LLETZ in this model.Surgical novices and experts were recruited and were shown a LLETZ training video and then performed 3 LLETZ training sessions on consecutive days. Surgical skills were assessed by Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS). Global rating scale (GRS), confidence (CON), fragmentation rate (FR), performance time (PT), and OSATS scores were calculated. Intra- and interobserver variabilities were determined. The construct validity of OSATS was assessed comparing metric scores of novices with those of experts.Sixty-eight probands (58 novices, 10 experts) were recruited. GRS, 2.3 ± 1.3 (median ± SD) versus 1.4 ± 0.6, P < .001; CON, 2.7 ± 0.9 versus 1.6 ± 0.6, P < .001; FR, 81% versus 100%, P < .001; PT, 152 ± 33 versus 120 ± 27 seconds, P = .006; and OSATS scores, 18.8 ± 1.3 versus 19.1 ± 1.1, P = .16 of novices improved from session 1 to session 3. OSATS showed construct validity with metric scores (GRS, 1.1 ± 0.3 vs 2.3 ± 0.8, P < .001; CON, 1.0 ± 0.0 vs 2.7 ± 0.9, P < .001; PT 125 ± 30 vs 152 ± 33 seconds, P = .02; OSATS scores, 19.6 ± 0.7 vs. 18.8 ± 1.3, P = .02) reliably discriminating between experts and novices. Intra- and interobserver variabilities across probands were 0.99 ± 0.03 and 0.64 ± 0.10, respectively. OSATS scores were independent of handedness, sex, and regular sports activity in univariate and multivariate analyses.Repeated hands-on trainings improve surgical performance of LLETZ in a surgical training model with construct validity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized comparison of video demonstration versus hands-on training of medical students for vacuum delivery using Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS).Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Mar;96(11):e6355. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006355. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28296771 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Direct Observation versus Endoscopic Video Recording-Based Rating with the Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills for Training of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.Eur Surg Res. 2016;57(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1159/000444449. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Eur Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27058392
-
Construct Validity of a Simple Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy Model Using a Validated Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017 Jul-Aug;24(5):850-854. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 17. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017. PMID: 28526619
-
Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS) evaluation of hysteroscopy training: a prospective study.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014 Jul;178:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2014.04.032. Epub 2014 May 9. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014. PMID: 24948046
-
Objective Structured Assessments of Technical Skills (OSATS) Does Not Assess the Quality of the Surgical Result Effectively.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Apr;474(4):874-81. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4603-4. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26502107 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A method to improve the accuracy between the presumed depth of excision and the actual depth of excision in women receiving LLETZ cervical treatment; a single-center, two-operator experience.Hippokratia. 2018 Jul-Sep;22(3):113-121. Hippokratia. 2018. PMID: 31642448 Free PMC article.
-
Operator Sex and Experience Do Not Influence Conization Outcomes in Terms of Cone Volume, Depth or Resection Margins.In Vivo. 2023 Mar-Apr;37(2):841-847. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13151. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 36881101 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating a novel 3D printed model for simulating Large Loop Excision of the Transformation Zone (LLETZ).3D Print Med. 2022 Jun 8;8(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s41205-022-00143-x. 3D Print Med. 2022. PMID: 35674843 Free PMC article.
-
Introducing a novel model for simulating large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) using 3D printing technique.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022 Mar;305(3):703-712. doi: 10.1007/s00404-021-06209-1. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 34491415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2-3 and adenocarcinoma in situ: Cryotherapy, large loop excision of the transformation zone, and cold knife conization. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014. - PubMed
-
- Lindeque BG. Management of cervical premalignant lesions. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2005;19:545–61. - PubMed
-
- Hefler L, Grimm C, Kueronya V, et al. A novel training model for the loop electrosurgical excision procedure: an innovative replica helped workshop participants improve their LEEP. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;206:535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

