Relationship of Treg/Th17 balance with HBeAg change in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving telbivudine antiviral treatment: A longitudinal observational study
- PMID: 28591041
- PMCID: PMC5466219
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007064
Relationship of Treg/Th17 balance with HBeAg change in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving telbivudine antiviral treatment: A longitudinal observational study
Abstract
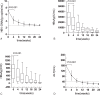
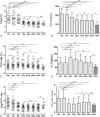
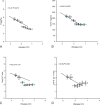
Telbivudine (LdT) is an orally L-nucleoside with potent and specific antihepatitis B virus (HBV) activity. The higher rate of hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion of LdT treatment than other anti-HBV agents suggests a potential immunomodulatory effect. The aim of the study was to investigate the changes of regulatory T cell (Treg)/interleukin (IL)-17-producing CD4+T helper (Th17) balance during LdT treatment and to discuss the relationship of Treg/Th17 balance with HBeAg change in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients receiving LdT antiviral treatment. Twenty-seven HBeAg-positive CHB patients received LdT for 24 weeks and the percentages of Tregs and cells (Th17 cells) in peripheral blood as well as the serum TGF-β1 and IL-17 levels in these patients were longitudinally analyzed. We found that the frequencies of Tregs and Th17 cells in peripheral blood as well as the serum TGF-β1 and IL-17 levels increased significantly in CHB patients compared with healthy controls. During the LdT treatment, the Tregs frequency and TGF-β1 level tended to decrease, and Th17 cells frequency and IL-17 level showed a reverse "V"-type change. The frequency of Tregs and the ratio of Treg/Th17 were significantly lower in the HBeAg loss group than those in the HBeAg no-loss group at the baseline. More important, the Tregs frequency and TGF-β1 level were both positively correlated with HBeAg level during the LdT treatment for 24 weeks. Our data suggest that the lower Tregs frequency and Treg/Th17 ratio at the baseline of LdT treatment, the more likely to get the HBeAg loss. HBeAg negative can be predicted using changes in Tregs frequency and TGF-β1 level during LdT treatment in CHB patients. Maybe we could provide the immunology marker for exploring the mechanism of the higher HBeAg seroconversion rate of LdT therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low Ratio of Treg to Th17 Cells After 36 Weeks of Telbivudine Therapy Predict HBeAg Seroconversion.Viral Immunol. 2016 Jul-Aug;29(6):332-42. doi: 10.1089/vim.2016.0007. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Viral Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27104358
-
Viral infection parameters not nucleoside analogue itself correlates with host immunity in nucleoside analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 28;20(28):9486-96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9486. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25071343 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serum interleukin-37 concentrations and HBeAg seroconversion in chronic HBV patients during telbivudine treatment.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013 Oct;33(10):612-8. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0001. Epub 2013 May 22. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013. PMID: 23697556 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of telbivudine and entecavir for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Nov 21;18(43):6290-301. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6290. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23180951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telbivudine treatment is associated with high hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion and immune modulatory effects in chronic hepatitis B patients.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Apr;20 Suppl 1:9-17. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12059. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23458520 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Regulatory T Cells in Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain 2 Response to Influenza Virus Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 31;9:132. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00132. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29445379 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of prophylactic antiviral intervention on T cell immunity in hepatitis B virus-infected pregnant women.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 May 27;23(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-05700-8. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37245038 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic Analysis of Prognostic and Immune-Related Genes in Pancreatic Cancer.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Aug 3;2021:5549298. doi: 10.1155/2021/5549298. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34394706 Free PMC article.
-
The Connection between MiR-122 and Lymphocytes in Patients Receiving Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 8;11(11):2731. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112731. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004743 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of pegylated interferon-alpha and nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment enhances the activity of natural killer cells in nucleos(t)ide analogue experienced chronic hepatitis B patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2020 Oct;202(1):80-92. doi: 10.1111/cei.13486. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32638357 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2009;373:582–92. - PubMed
-
- Maini MK, Boni C, Ogg GS, et al. Direct ex vivo analysis of hepatitis B virus specific CD8+T cells associated with the control of infection. Gastroenterology 1999;117:1386–96. - PubMed
-
- Wang FS, Zhang Z. Host immunity influences disease progression and antiviral efficacy in humans infected with hepatitis B virus. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;3:499–512. - PubMed
-
- Rehermann B, Nascimbeni M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol 2005;5:215–29. - PubMed
-
- Bertoletti A, Naoumov NV. Translation of immunological knowledge into better treatments of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2003;39:115–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

