Maintenance of cancer stemness by miR-196b-5p contributes to chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells via activating STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 28591704
- PMCID: PMC5564809
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17971
Maintenance of cancer stemness by miR-196b-5p contributes to chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells via activating STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
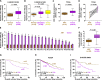
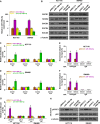
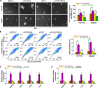
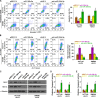
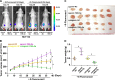
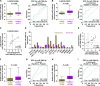
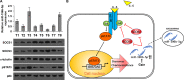
Emerging studies indicated that cancer stem cells represent a subpopulation of cells within the tumor that is responsible for chemotherapeutic resistance. However, the underlying mechanism is still not clarified yet. Here we report that miR-196b-5p is dramatically upregulated in CRC tissues and high expression of miR-196b-5p correlates with poor survival in CRC patients. Moreover, recurrent gains (amplification) contribute to the miR-196b-5p overexpression in CRC tissues. Silencing miR-196b-5p suppresses spheroids formation ability, the fraction of SP cells, expression of stem cell factors and the mitochondrial potential, and enhances the apoptosis induced by 5-fluorouracil in CRC cells; while ectopic expression of miR-196b-5p yields an opposite effect. In addition, downregulation of miR-196b-5p resensitizes CRC cells to 5-fluorouracil in vivo. Our results further demonstrate that miR-196b-5p promotes stemness and chemoresistance of CRC cells to 5-fluorouracil via targeting negative regulators SOCS1 and SOCS3 of STAT3 signaling pathway, giving rise to activation of STAT3 signaling. Interestingly, miR-196b-5p is highly enriched in the serum exosomes of patients with CRC compared to the healthy control subjects. Thus, our results unravel a novel mechanism of miR-196b-5p implicating in the maintenance of stem cell property and chemotherapeutic resistance in CRC, offering a potential rational registry of anti-miR-196b-5p combining with conventional chemotherapy against CRC.
Keywords: CRC; STAT3 signaling pathway; cancer stem cell; chemotherapeutic resistance; miR-196b-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Ricci-Vitiani L, Fabrizi E, Palio E, De Maria R. Colon cancer stem cells. J Mol Med (Berl) 2009;87:1097–1104. - PubMed
-
- Thota R, Pauff JM, Berlin JD. Treatment of metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a review. Oncology (Williston Park) 2014;28:70–74. - PubMed
-
- Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD, Dirks PB. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432:396–401. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

