Adapting AlphaLISA high throughput screen to discover a novel small-molecule inhibitor targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 in pancreatic and colorectal cancers
- PMID: 28591716
- PMCID: PMC5522311
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18102
Adapting AlphaLISA high throughput screen to discover a novel small-molecule inhibitor targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 in pancreatic and colorectal cancers
Abstract
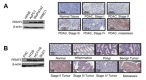
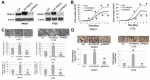
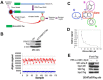
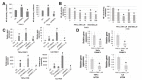
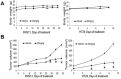
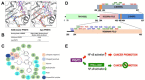
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and colorectal cancer (CRC) are notoriously challenging for treatment. Hyperactive nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) is a common culprit in both cancers. Previously, we discovered that protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) methylated and activated NF-κB. Here, we show that PRMT5 is highly expressed in PDAC and CRC. Overexpression of PRMT5 promoted cancer progression, while shRNA knockdown showed an opposite effect. Using an innovative AlphaLISA high throughput screen, we discovered a lead compound, PR5-LL-CM01, which exhibited robust tumor inhibition effects in both cancers. An in silico structure prediction suggested that PR5-LL-CM01 inhibits PRMT5 by binding with its active pocket. Importantly, PR5-LL-CM01 showed higher anti-tumor efficacy than the commercial PRMT5 inhibitor, EPZ015666, in both PDAC and CRC. This study clearly highlights the significant potential of PRMT5 as a therapeutic target in PDAC and CRC, and establishes PR5-LL-CM01 as a promising basis for new drug development in the future.
Keywords: AlphaLISA; PRMT5; colorectal cancer; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; small-molecule inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare conflicting financial interest; PR5-LL-CM01 has been filed for provisional patent on October 26, 2016.
Figures

References
-
- Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardiere C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1817–25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1011923. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

