Riluzole exerts distinct antitumor effects from a metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-specific inhibitor on breast cancer cells
- PMID: 28591718
- PMCID: PMC5546507
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17961
Riluzole exerts distinct antitumor effects from a metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-specific inhibitor on breast cancer cells
Abstract
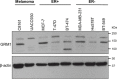
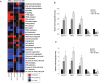
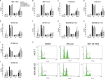
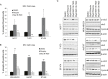
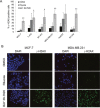
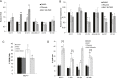
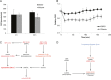
Recent evidence suggests that glutamate signaling plays an important role in cancer. Riluzole is a glutamate release inhibitor and FDA-approved drug for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It has been investigated as an inhibitor of cancer cell growth and tumorigenesis with the intention of repurposing it for the treatment of cancer. Riluzole is thought to act by indirectly inhibiting glutamate signaling. However, the specific effects of riluzole in breast cancer cells are not well understood. In this study, the anti-cancer effects of riluzole were explored in a panel of breast cancer cell lines in comparison to the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-specific inhibitor BAY 36-7620. While both drugs inhibited breast cancer cell proliferation, there were distinct functional effects suggesting that riluzole action may be metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-independent. Riluzole induced mitotic arrest independent of oxidative stress while BAY 36-7620 had no measurable effect on mitosis. BAY 36-7620 had a more pronounced and significant effect on DNA damage than riluzole. Riluzole altered cellular metabolism as demonstrated by changes in oxidative phosphorylation and cellular metabolite levels. These results provide a better understanding of the functional action of riluzole in the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: BAY 36-7620; breast cancer; cell cycle; glutamate signaling; riluzole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Riluzole mediates anti-tumor properties in breast cancer cells independent of metabotropic glutamate receptor-1.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jun;157(2):217-228. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3816-x. Epub 2016 May 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27146584
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor-1: a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(2):565-73. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1624-x. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21681448 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate release inhibitor, Riluzole, inhibited proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by elevated ROS production.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 28;382(2):157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.028. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27612558
-
Riluzole: A neuroprotective drug with potential as a novel anti‑cancer agent (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Nov;59(5):95. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5275. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34713302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors in cancer.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Mar 15;115:193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.02.011. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 26896755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering immune cell-associated genes in breast cancer: based on summary data-based Mendelian randomized analysis and colocalization study.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 29;26(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01928-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39614330 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing riluzole as an anti-osteosarcoma agent.Front Oncol. 2025 May 5;15:1508819. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1508819. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40391158 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic Signaling a Therapeutic Vulnerability in Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 31;13(15):3874. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153874. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current State of Melanoma Therapy and Next Steps: Battling Therapeutic Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;16(8):1571. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081571. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Riluzole regulates pancreatic cancer cell metabolism by suppressing the Wnt-β-catenin pathway.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 30;12(1):11062. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13472-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35773307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teh JL, Chen S. Glutamatergic signaling in cellular transformation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012;25:331–342. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

