Clinical safety and efficacy of vitamin D3 analog ointment for treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction
- PMID: 28592257
- PMCID: PMC5463421
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-017-0482-7
Clinical safety and efficacy of vitamin D3 analog ointment for treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Hyperkeratinization is a major cause of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction (oMGD) and results in degenerative gland dilation and atrophy without inflammation. Ointment containing 1,25-dihydroxy-22-oxavitamin D3 (maxacalcitol), a noncalcemic analog of the active form of vitamin D3, is applied for the treatment of hyperkeratotic cutaneous conditions such as psoriasis and ichtyosis because it suppresses the proliferation and promotes the differentiation of keratinocytes through interaction with the vitamin D receptor. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of maxacalcitol ointment for the treatment of oMGD.
Methods: Six eyes of six healthy male subjects (mean age ± SD, 36.4 ± 10.8 years) and 12 eyes of eight oMGD patients (five men and three women; mean age ± SD, 55.6 ± 13.2 years) were enrolled in the study. Maxacalcitol ointment was applied to the upper and lower lid margins twice a day for 8 weeks. Subjective symptoms, lid margin abnormalities, tear film breakup time (BUT), ocular surface staining, meibum grade, Schirmer test value, and meibomian gland area were evaluated in the oMGD patients before, during, and after the treatment period.
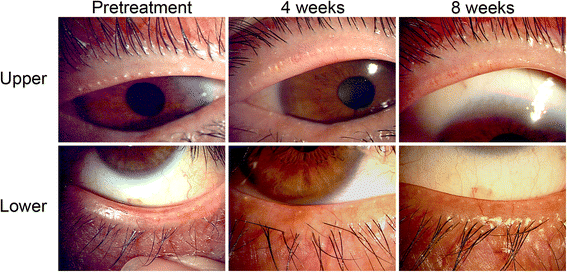
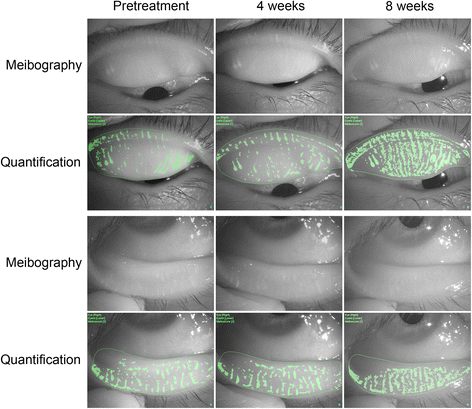
Results: Severe adverse effects of ointment application were not observed in the healthy subjects or oMGD patients. The clinical scores for plugging of meibomian gland orifices and lid margin vascularity as well as BUT, meibum grade, and meibomian gland area were significantly improved in oMGD patients after the 8-week treatment period compared with pretreatment values (P values of <0.001, 0.020, 0.030, 0.020, and 0.017, respectively).
Conclusions: Topical eyelid application of an analog of the active form of vitamin D3 was found to be safe as well as to improve the condition of patients with oMGD. Such ointment thus warrants further evaluation as a potential new treatment option for this condition.
Trial registration: This study was registered with the UMIN database (ID: UMIN000016230 ) on 16 January 2015.
Keywords: Meibomian gland dysfunction; Meibomian gland obstruction; Ointment; Vitamin D3.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eyelid cleansing with ointment for obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017 Jan;61(1):124-130. doi: 10.1007/s10384-016-0477-6. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 27699522
-
Effect of Eyelid Hygiene Detergent on Obstructive Meibomian Gland Dysfunction.J Oleo Sci. 2019 Jan 1;68(1):67-78. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess18161. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Oleo Sci. 2019. PMID: 30542004
-
Evaluation of vitamin D and serum lipid profile levels in obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2025 Apr;48(4):104467. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2025.104467. Epub 2025 Mar 7. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2025. PMID: 40056767
-
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Contact Lens Discomfort.Eye Contact Lens. 2017 Jan;43(1):17-22. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000351. Eye Contact Lens. 2017. PMID: 28002224 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of topical calcitriol 3 microg/g ointment, a new topical therapy for chronic plaque psoriasis.J Drugs Dermatol. 2009 Aug;8(8 Suppl):s9-16. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19702031 Review.
Cited by
-
Relation of Dietary Fatty Acids and Vitamin D to the Prevalence of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Japanese Adults: The Hirado-Takushima Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 18;10(2):350. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020350. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33477594 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, Tear Film, and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Facial Palsy: A Comparative Analysis.Clin Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan 8;19:93-100. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S481124. eCollection 2025. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39801571 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Ocular Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 11;23(8):4226. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084226. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457041 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of meibomian glands in childhood malnutrition.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23117. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09216-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40604071 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Advances in the Treatment of Skin Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;14(11):1083. doi: 10.3390/ph14111083. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

