Potential survival benefit of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in patients with septic shock: a propensity-matched cohort study
- PMID: 28592318
- PMCID: PMC5463489
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1712-3
Potential survival benefit of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in patients with septic shock: a propensity-matched cohort study
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate whether polymyxin B hemoperfusion (PMX-HP) improves the survival of patients with septic shock.
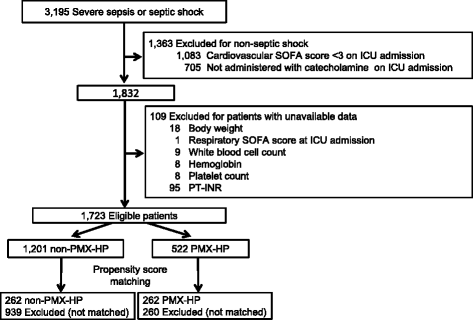
Methods: This was a retrospective, multicenter study conducted on patients treated during a 3-year period. We performed propensity-score analyses of the Japan Septic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (JSEPTIC DIC) study database. The study included data on 1723 patients with septic shock aged 16 years or older. Furthermore, we divided patients into to PMX-HP- and non-PMX-HP-treated groups. The primary endpoint was all-cause hospital mortality; secondary endpoints included intensive care unit (ICU) mortality and number of ICU-free days (ICUFDs) in the first 28 days.
Results: Of 1,723 eligible patients, 522 had received PMX-HP. Propensity score matching created 262 matched pairs (i.e., 262 patients in each of the non-PMX-HP and PMX-HP groups). The proportion of all-cause hospital mortality was significantly lower in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group (32.8% vs. 41.2%; odds ratio (OR): 0.681; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.470-0.987; P = 0.042). The number of ICUFD in the first 28 days was significantly higher in the PMX-HP group than in the non-PMX-HP group (18 (0-22) vs. 14 (0-22) days, respectively; P = 0.045). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in ICU mortality between the two groups (21.8% vs. 24.4%; OR: 0.844; CI: 0.548-1.300; P = 0.443).
Conclusions: Our results strongly suggest that PMX-HP reduces all-cause hospital mortality and length of ICU stay in patients with septic shock.
Keywords: Intensive care unit-free days; Mortality; Polymyxin B hemoperfusion; Propensity score matching; Septic shock.
Figures
Comment in
-
Polymyxin B hemoperfusion in septic shock: nothing overmuch (Meden Agan)!J Thorac Dis. 2017 Sep;9(9):2716-2719. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.08.106. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 29221222 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Efficacy of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in and beyond septic shock: is an "endotoxin severity score" needed?Crit Care. 2018 Aug 17;22(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2093-y. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30115067 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Time to administer polymyxin B hemoperfusion and hemodynamics in patients with septic shock requiring high-dose norepinephrine: a predetermined analysis of a prospective cohort study.Crit Care. 2025 May 9;29(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13054-025-05422-7. Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 40346574 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion on Septic Shock Patients Requiring Noradrenaline: Analysis of a Nationwide Administrative Database in Japan.Blood Purif. 2021;50(4-5):560-565. doi: 10.1159/000513213. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Blood Purif. 2021. PMID: 33582663
-
VASOPRESSOR REDUCTION EFFECT OF POLYMYXIN B HEMOPERFUSION IN PATIENTS WITH PERITONITIS-INDUCED SEPTIC SHOCK: A PROPENSITY SCORE-MATCHED ANALYSIS.Shock. 2024 Jul 1;62(1):69-73. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002375. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Shock. 2024. PMID: 38661146
-
Polymyxin B-immobilized hemoperfusion and mortality in critically ill adult patients with sepsis/septic shock: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Intensive Care Med. 2018 Feb;44(2):167-178. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-5004-9. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Intensive Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29204670
-
Effectiveness of polymyxin B-immobilized hemoperfusion against sepsis and septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Crit Care. 2021 Jun;63:187-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.09.007. Epub 2020 Sep 18. J Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33012579
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion for Treatment of Sepsis.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024 Oct;28(10):930-934. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24805. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39411305 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine modulation in abdominal septic shock via the crucial role of IL-6 signaling in endothelial dysfunction.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 1;10:1042487. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1042487. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37007795 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Sepsis: A Possible Silver Lining to the Dark Clouds?Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024 Oct;28(10):903-905. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24816. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39411302 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effect modification on survival outcome of sepsis between ART-123 and polymyxin B‑immobilised haemoperfusion: a nationwide Japanese registry study.Ann Intensive Care. 2020 May 13;10(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00674-8. Ann Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 32405776 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Rationale for Endotoxin Removal with Polymyxin B Immobilized Fiber Column (PMX) for Septic Shock.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 23;22(4):2228. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042228. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Deventer SJ, Buller HR, ten Cate JW, Aarden LA, Hack CE, Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990;76:2520–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous