Transgenic tomatoes expressing the 6F peptide and ezetimibe prevent diet-induced increases of IFN-β and cholesterol 25-hydroxylase in jejunum
- PMID: 28592401
- PMCID: PMC5538285
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M076554
Transgenic tomatoes expressing the 6F peptide and ezetimibe prevent diet-induced increases of IFN-β and cholesterol 25-hydroxylase in jejunum
Abstract
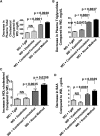
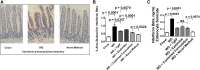
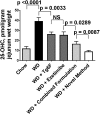
Feeding LDL receptor (LDLR)-null mice a Western diet (WD) increased the expression of IFN-β in jejunum as determined by quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and ELISA (all P < 0.0001). WD also increased the expression of cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H) as measured by RT-qPCR (P < 0.0001), IHC (P = 0.0019), and ELISA (P < 0.0001), resulting in increased levels of 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OHC) in jejunum as determined by LC-MS/MS (P < 0.0001). Adding ezetimibe at 10 mg/kg/day or adding a concentrate of transgenic tomatoes expressing the 6F peptide (Tg6F) at 0.06% by weight of diet substantially ameliorated these changes. Adding either ezetimibe or Tg6F to WD also ameliorated WD-induced changes in plasma lipids, serum amyloid A, and HDL cholesterol. Adding the same doses of ezetimibe and Tg6F together to WD (combined formulation) was generally more efficacious compared with adding either agent alone. Surprisingly, adding ezetimibe during the preparation of Tg6F, but before addition to WD, was more effective than the combined formulation for all parameters measured in jejunum (P = 0.0329 to P < 0.0001). We conclude the following: i) WD induces IFN-β, CH25H, and 25-OHC in jejunum; and ii) Tg6F and ezetimibe partially ameliorate WD-induced inflammation by preventing WD-induced increases in IFN-β, CH25H, and 25-OHC.
Keywords: apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides; atherosclerosis; hyperlipidemia; oxysterols.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Oxidized phospholipids cause changes in jejunum mucus that induce dysbiosis and systemic inflammation.J Lipid Res. 2022 Jan;63(1):100153. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100153. Epub 2021 Nov 20. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 34808192 Free PMC article.
-
Tg6F ameliorates the increase in oxidized phospholipids in the jejunum of mice fed unsaturated LysoPC or WD.J Lipid Res. 2016 May;57(5):832-47. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M064352. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26965826 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic 6F tomatoes act on the small intestine to prevent systemic inflammation and dyslipidemia caused by Western diet and intestinally derived lysophosphatidic acid.J Lipid Res. 2013 Dec;54(12):3403-18. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M042051. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 24085744 Free PMC article.
-
The structure/function of apoprotein A-I mimetic peptides: an update.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014 Apr;21(2):129-33. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000045. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014. PMID: 24569554 Review.
-
An overview of rosuvastatin/ezetimibe association for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Apr;21(5):531-539. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1714028. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32036729 Review.
Cited by
-
Oral 15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Induces Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice by Triggering T Cell-Dependent Endothelial Cell Apoptosis.Hypertension. 2020 Sep;76(3):985-996. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14697. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32713273 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized phospholipids cause changes in jejunum mucus that induce dysbiosis and systemic inflammation.J Lipid Res. 2022 Jan;63(1):100153. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100153. Epub 2021 Nov 20. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 34808192 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I mimetics mitigate intestinal inflammation in COX2-dependent inflammatory bowel disease model.J Clin Invest. 2019 Jun 11;129(9):3670-3685. doi: 10.1172/JCI123700. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31184596 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Circulating Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Biomarkers.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 14;9:924873. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.924873. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35911521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial High Density Lipoprotein Nanoparticles in Cardiovascular Research.Molecules. 2019 Aug 2;24(15):2829. doi: 10.3390/molecules24152829. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31382521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Navab M., Anantharamaiah G. M., Hama S., Garber D. W., Chaddha M., Hough G., Lallone R., and Fogelman A. M.. 2002. Oral administration of an apo A-I mimetic peptide synthesized from D-amino acids dramatically reduces atherosclerosis in mice independent of plasma cholesterol. Circulation. 105: 290–292. - PubMed
-
- Navab M., Anantharamaiah G. M., Reddy S. T., Hama S., Hough G., Grijalva V. R., Wagner A. C., Frank J. S., Datta G., Garber D., et al. . 2004. Oral D-4F causes formation of pre-beta high-density lipoprotein and improves high-density lipoprotein mediated cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport from macrophages in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Circulation. 109: 3215–3220. - PubMed
-
- Navab M., Anantharamaiah G. M., Hama S., Hough G., Reddy S. T., Frank J. S., Garber D. W., Handattu S., and Fogelman A. M.. 2005. D-4F and statins synergize to render HDL anti-inflammatory in mice and monkeys and cause lesion regression in old apolipoprotein E-null mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25: 1426–1432. - PubMed
-
- Van Lenten B. J., Wagner A. C., Navab M., Anantharamaiah G. M., Hama S., Reddy S. T., and Fogelman A. M.. 2007. Lipoprotein inflammatory properties and serum amyloid A levels but not cholesterol levels predict lesion area in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J. Lipid Res. 48: 2344–2353. - PubMed
-
- Bloedon L. T., Dunbar R., Duffy D., Pinell-Salles P., Norris R., DeGroot B. J., Movva R., Navab M., Fogelman A. M., and Rader D. J.. 2008. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients. J. Lipid Res. 49: 1344–1352. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

