MicroRNAs of Epstein-Barr Virus Control Innate and Adaptive Antiviral Immunity
- PMID: 28592533
- PMCID: PMC5533892
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01667-16
MicroRNAs of Epstein-Barr Virus Control Innate and Adaptive Antiviral Immunity
Abstract
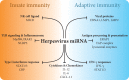
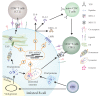
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has established lifelong infection in more than 90% of humanity. While infection is usually controlled by the immune system, the human host fails to completely eliminate the pathogen. Several herpesviral proteins are known to act as immunoevasins, preventing or reducing recognition of EBV-infected cells. Only recently were microRNAs of EBV identified to reduce immune recognition further. This Gem summarizes what we know about immunomodulatory microRNAs of herpesviruses.
Keywords: cancer; human herpesviruses; immune evasion; immune surveillance; microRNA.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Pfeffer S, Sewer A, Lagos-Quintana M, Sheridan R, Sander C, Grasser FA, van Dyk LF, Ho CK, Shuman S, Chien M, Russo JJ, Ju J, Randall G, Lindenbach BD, Rice CM, Simon V, Ho DD, Zavolan M, Tuschl T. 2005. Identification of microRNAs of the herpesvirus family. Nat Methods 2:269–276. doi:10.1038/nmeth746. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

