Oas1b-dependent Immune Transcriptional Profiles of West Nile Virus Infection in the Collaborative Cross
- PMID: 28592649
- PMCID: PMC5473748
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.117.041624
Oas1b-dependent Immune Transcriptional Profiles of West Nile Virus Infection in the Collaborative Cross
Abstract
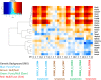
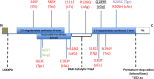
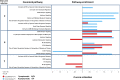
The oligoadenylate-synthetase (Oas) gene locus provides innate immune resistance to virus infection. In mouse models, variation in the Oas1b gene influences host susceptibility to flavivirus infection. However, the impact of Oas variation on overall innate immune programming and global gene expression among tissues and in different genetic backgrounds has not been defined. We examined how Oas1b acts in spleen and brain tissue to limit West Nile virus (WNV) susceptibility and disease across a range of genetic backgrounds. The laboratory founder strains of the mouse Collaborative Cross (CC) (A/J, C57BL/6J, 129S1/SvImJ, NOD/ShiLtJ, and NZO/HlLtJ) all encode a truncated, defective Oas1b, whereas the three wild-derived inbred founder strains (CAST/EiJ, PWK/PhJ, and WSB/EiJ) encode a full-length OAS1B protein. We assessed disease profiles and transcriptional signatures of F1 hybrids derived from these founder strains. F1 hybrids included wild-type Oas1b (F/F), homozygous null Oas1b (N/N), and heterozygous offspring of both parental combinations (F/N and N/F). These mice were challenged with WNV, and brain and spleen samples were harvested for global gene expression analysis. We found that the Oas1b haplotype played a role in WNV susceptibility and disease metrics, but the presence of a functional Oas1b allele in heterozygous offspring did not absolutely predict protection against disease. Our results indicate that Oas1b status as wild-type or truncated, and overall Oas1b gene dosage, link with novel innate immune gene signatures that impact specific biological pathways for the control of flavivirus infection and immunity through both Oas1b-dependent and independent processes.
Keywords: MPP; Multi-parent Advanced Generation Inter-Cross (MAGIC); Oas; flavivirus; innate immunity; multiparental populations; viral infection.
Copyright © 2017 Green et al.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Genetic diversity in the collaborative cross model recapitulates human West Nile virus disease outcomes.mBio. 2015 May 5;6(3):e00493-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00493-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25944860 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic expression of full-length 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 1b confers to BALB/c mice resistance against West Nile virus-induced encephalitis.Virology. 2011 Aug 15;417(1):147-53. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21683973
-
Infection of mouse neurones by West Nile virus is modulated by the interferon-inducible 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase 1b protein.Immunol Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;81(3):230-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2003.01166.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12752688
-
Innate resistance to flavivirus infections and the functions of 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;321:85-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75203-5_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18727488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Immune Aging in Susceptibility to West Nile Virus.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1435:235-47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3670-0_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27188562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Collaborative Cross mouse model for dissecting genetic susceptibility to infectious diseases.Mamm Genome. 2018 Aug;29(7-8):471-487. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9768-1. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Mamm Genome. 2018. PMID: 30143822 Review.
-
Neuroinvasive Flavivirus Pathogenesis Is Restricted by Host Genetic Factors in Collaborative Cross Mice, Independently of Oas1b.J Virol. 2023 Jul 27;97(7):e0071523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00715-23. Epub 2023 Jun 13. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37310228 Free PMC article.
-
A chromosome-level genome assembly of the Hispid cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus), a model for human pathogenic virus infections.BMC Biol. 2025 Jul 18;23(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02316-6. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40682131 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience in Long-Term Viral Infection: Genetic Determinants and Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 21;22(21):11379. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111379. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768809 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Faces of Oligoadenylate Synthetases.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023 Nov;43(11):487-494. doi: 10.1089/jir.2023.0098. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023. PMID: 37751211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bottomly D., Wilmot B., McWeeney S. K. 2014. Oligomask: a framework for assessing and removing the effect of genetic variants on microarray probes. R J. 6(1): 159–163.
-
- Brinton M. A., Perelygin A. A., 2003. Genetic resistance to flaviviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 60: 43–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
