Cdc6 contributes to abrogating the G1 checkpoint under hypoxic conditions in HPV E7 expressing cells
- PMID: 28592805
- PMCID: PMC5462782
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03060-w
Cdc6 contributes to abrogating the G1 checkpoint under hypoxic conditions in HPV E7 expressing cells
Abstract
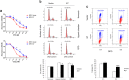
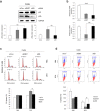
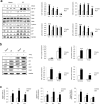
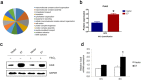
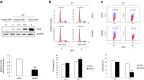
The human papillomavirus (HPV) plays a central role in cervical carcinogenesis and its oncogene E7 is essential in this process. We showed here that E7 abrogated the G1 cell cycle checkpoint under hypoxia and analyzed key cell cycle related proteins for their potential role in this process. To further explore the mechanism by which E7 bypasses hypoxia-induced G1 arrest, we applied a proteomic approach and used mass spectrometry to search for proteins that are differentially expressed in E7 expressing cells under hypoxia. Among differentially expressed proteins identified, Cdc6 is a DNA replication initiation factor and exhibits oncogenic activities when overexpressed. We have recently demonstrated that Cdc6 was required for E7-induced re-replication. Significantly, here we showed that Cdc6 played a role in E7-mediated G1 checkpoint abrogation under hypoxic condition, and the function could possibly be independent from its role in DNA replication initiation. This study uncovered a new function of Cdc6 in regulating cell cycle progression and has important implications in HPV-associated cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of WDHD1 in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Oncogenesis Identified by Transcriptional Profiling of E7-Expressing Cells.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):6071-6084. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00513-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27099318 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of chromatin condensation 1 abrogates the G1 cell cycle checkpoint via Cdk1 in human papillomavirus E7-expressing epithelium and cervical cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 22;9(6):583. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0584-z. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29789527 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cdc6 in re-replication in cells expressing human papillomavirus E7 oncogene.Carcinogenesis. 2016 Aug;37(8):799-809. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgw059. Epub 2016 May 6. Carcinogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27207654 Free PMC article.
-
The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein as a regulator of transcription.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:56-75. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.10.017. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27818212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HPV E6/E7 Oncogenes: Key Factors for Viral Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Targets.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Feb;26(2):158-168. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28823569 Review.
Cited by
-
The lysine acetyltransferase GCN5 contributes to human papillomavirus oncoprotein E7-induced cell proliferation via up-regulating E2F1.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Nov;22(11):5333-5345. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13806. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30079588 Free PMC article.
-
Metadata analysis to explore hub of the hub-genes highlighting their functions, pathways and regulators for cervical cancer diagnosis and therapies.Discov Oncol. 2022 Aug 22;13(1):79. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00546-6. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35994213 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-induced suppression of HPV E6/E7 is mediated by microRNA-9-5p silencing of BRD4 protein in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 4;13(11):921. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05269-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36333293 Free PMC article.
-
The Not-So-Good, the Bad and the Ugly: HPV E5, E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in the Orchestration of Carcinogenesis.Viruses. 2021 Sep 22;13(10):1892. doi: 10.3390/v13101892. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics Screening of Potential Biomarkers from mRNA Expression Profiles to Discover Drug Targets and Agents for Cervical Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 2;23(7):3968. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073968. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409328 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

