The Effects of e-interventions on the Medical Outcomes of Hemodialysis Patients: A Retrospective Matched Patient Cohort Study
- PMID: 28592842
- PMCID: PMC5462823
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02815-9
The Effects of e-interventions on the Medical Outcomes of Hemodialysis Patients: A Retrospective Matched Patient Cohort Study
Abstract
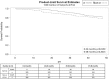
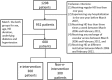
Aggressively applying e-interventions in the health care industry has become a global trend to improve the quality of medical care. The present retrospective study evaluated the effect of electronic information systems on the quality of medical care provide to hemodialysis (HD) patients. In total, 600 patients (300 patients each in the e-intervention and non-e-intervention groups, were matched for sex, age, HD duration, diabetes, and hypertension) receiving HD at the study institute for four years were included in this study. The e-intervention group had significantly fewer hospitalization days than the non-e-intervention group. Cox regression analysis demonstrated that the non-e-intervention group had a significantly higher mortality rate than the e-intervention group. Stratified analysis revealed significant differences between the e-intervention and non-e-intervention groups in their serum albumin levels, urea reduction ratios, and cardiothoracic ratios at 1-year follow-up. The patients in the e-intervention group had a significantly higher HD blood flow rate, fewer hospitalization days and a lower 4-year all-cause mortality rate than those in the non-e-intervention group. The implementation of the e-intervention improved patient outcomes, but additional studies are required to evaluate the cost effectiveness of such implementations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effects of two early intervention strategies on the health outcomes of malnourished hemodialysis patients.J Ren Nutr. 2001 Jul;11(3):166-71. doi: 10.1053/jren.2001.24364. J Ren Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11466668
-
The effect of technique failure on outcome in black patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.Perit Dial Int. 2002 Jan-Feb;22(1):53-9. Perit Dial Int. 2002. PMID: 11929145
-
[The Veneto Region's Registry of Dialysis and Transplantation: 2006-2007 report].G Ital Nefrol. 2009 Nov-Dec;26 Suppl 48:S5-56. G Ital Nefrol. 2009. PMID: 19927265 Italian.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular stent grafting and open surgical replacement for chronic thoracic aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and prospective cohort study.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Jan;26(6):1-166. doi: 10.3310/ABUT7744. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 35094747
Cited by
-
Causes of Hospitalization among End-Stage Kidney Disease Cohort before and after Hemodialysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 18;19(16):10253. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191610253. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36011888 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

