Incorporation of Fluorescence Ceramide-Based HPLC Assay for Rapidly and Efficiently Assessing Glucosylceramide Synthase In Vivo
- PMID: 28592871
- PMCID: PMC5462733
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03320-9
Incorporation of Fluorescence Ceramide-Based HPLC Assay for Rapidly and Efficiently Assessing Glucosylceramide Synthase In Vivo
Abstract
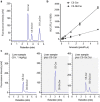
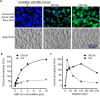
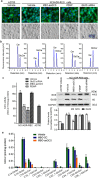
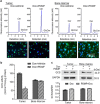
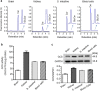
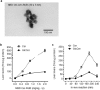
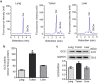
Glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) is a rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing ceramide glycosylation, thereby regulating cellular ceramide levels and the synthesis of glycosphingolipids (GSLs) in cellular membranes. Alterations of GCS not only affect membrane integrity, but also closely correlate with stem cell pluripotency, cancer drug resistance, GSL storage disorders and other diseases. Enzyme activities measured conventionally with currently available ex-vivo methods do not enable reliable assessment of the roles played by GCS in vivo. We report herein a substrate-incorporation method enabling rapid and efficient assessment of GCS in-vivo activity. Upon nanoparticle-based delivery, fluorescent NBD C6-ceramide was efficiently converted to NBD C6-glucosylceramide in live cells or in mouse tissues, whereupon an HPLC assay enabled detection and quantification of NBD C6-glucosylceramide in the low-femtomolar range. The enzyme kinetics of GCS in live cells and mouse liver were well-described by the Michaelis-Menten model. GCS activities were significantly higher in drug-resistant cancer cells and in tumors overexpressing GCS, but reduced after silencing GCS expression or inhibiting this enzyme. Our studies indicate that this rapid and efficient method provides a valuable means for accurately assessing the roles played by GCS in normal vs. pathological states, including ones involving cancer drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Basu S, Kaufman B, Roseman S. Enzymatic synthesis of ceramide-glucose and ceramide-lactose by glycosyltransferases from embryonic chicken brain. J Biol Chem. 1968;243:5802–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

