The lateral distance between a proton pump and ATP synthase determines the ATP-synthesis rate
- PMID: 28592883
- PMCID: PMC5462737
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02836-4
The lateral distance between a proton pump and ATP synthase determines the ATP-synthesis rate
Abstract
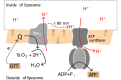
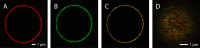
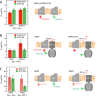
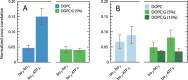
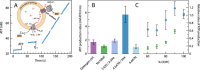
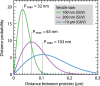
We have investigated the effect of lipid composition on interactions between cytochrome bo 3 and ATP-synthase, and the ATP-synthesis activity driven by proton pumping. The two proteins were labeled by fluorescent probes and co-reconstituted in large (d ≅ 100 nm) or giant (d ≅ 10 µm) unilamellar lipid vesicles. Interactions were investigated using fluorescence correlation/cross-correlation spectroscopy and the activity was determined by measuring ATP production, driven by electron-proton transfer, as a function of time. We found that conditions that promoted direct interactions between the two proteins in the membrane (higher fraction DOPC lipids or labeling by hydrophobic molecules) correlated with an increased activity. These data indicate that the ATP-synthesis rate increases with decreasing distance between cytochrome bo 3 and the ATP-synthase, and involves proton transfer along the membrane surface. The maximum distance for lateral proton transfer along the surface was found to be ~80 nm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gutman M, Nachliel E. The Dynamics of Proton-Exchange between Bulk and Surface Groups. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1231:123–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(95)00074-S. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

