Enhancement of Th1/Th17 inflammation by TRIM21 in Behçet's disease
- PMID: 28592884
- PMCID: PMC5462739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03251-5
Enhancement of Th1/Th17 inflammation by TRIM21 in Behçet's disease
Abstract
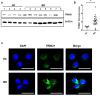
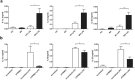
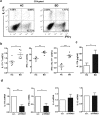
The etiology of Behçet's disease (BD), a chronic, multisystemic autoinflammatory and autoimmune disease, remains unknown; however, researchers have postulated that infectious agents, such as herpes simplex virus, are significant triggering factors of BD. Tripartite motif-containing (TRIM) proteins exhibit antiviral properties, mediating antiviral defense mechanisms. The purpose of this study was to investigate TRIM21 protein expression in the monocytes of BD patients and to identify the role of TRIM21 in immune dysregulation in BD. In this study, the expression of TRIM21 and related molecules, including interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8), was analyzed in monocytes from BD patients. Functional analyses using small interfering RNA and co-culture with responder T cells were performed to examine the pathological role of TRIM21 in BD. Peripheral blood monocytes from BD patients showed increased TRIM21 expression and decreased IRF8 expression compared with that in monocytes from healthy controls. TRIM21 was found to decrease IRF8 expression. BD monocytes facilitated Th1 and Th17 differentiation of co-cultured T cells, and knock-down of TRIM21 expression by small interfering RNA inhibited this differentiation. In conclusion, TRIM21 played a pivotal role in regulating the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in monocytes of BD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

