High Expression of Galectin-3 in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease: A Proteomic Approach
- PMID: 28593065
- PMCID: PMC5448067
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9312142
High Expression of Galectin-3 in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease: A Proteomic Approach
Abstract
Objectives: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a multiorgan condition manifesting itself in different forms. This study aimed to investigate protein expression profiles and to find the possible biomarker for IgG4-RD by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) using tissue sections in IgG4-RD patients.
Methods: Protein expression profiles in five IgG4-related pancreatitis and three normal pancreatic samples were compared using LC-MS and were validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), immunoblotting, and immunohistochemistry. ELISA was employed in the serum of 20 patients with systemic IgG4-RD before and during steroid treatment.
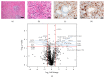
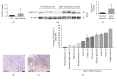
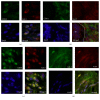
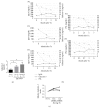
Results: LC-MS indicated that the levels of 17 proteins were significantly higher and 12 others were significantly lower in IgG4-related pancreatitis patients compared to controls. Among these proteins, galectin-3 levels were 13-fold higher in IgG4-related pancreatitis (P < 0.01). These results were confirmed by immunoblotting and qRT-PCR. The average number of galectin-3 + cells in various organs of IgG4-RD patients, including salivary glands, lungs, and lymph nodes, was higher than in controls. Galectin-3 was detectable in macrophages, dendritic cells, and stromal myofibroblast-like cells, but not in lymphocytes by immunofluorescence staining. Serum galectin-3 levels were higher in patients with IgG4-RD compared with healthy donors and remained high during steroid therapy.
Conclusion: Galectin-3 was overexpressed in IgG4-RD and the levels were indirectly related to clinical activity.
Figures
References
-
- Punnonen J., Aversa G., Cocks B. G., et al. Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1993;90(8):3730–3734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

