Nano-hemostats and a Pilot Study of Their Use in a Large Animal Model of Major Vessel Hemorrhage in Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery
- PMID: 28593108
- PMCID: PMC5461165
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1597277
Nano-hemostats and a Pilot Study of Their Use in a Large Animal Model of Major Vessel Hemorrhage in Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery
Abstract
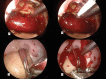
Nano-hemostats are synthetic amino acid chains that self-assemble into a scaffold under certain conditions. These have been shown to be effective in stopping bleeding in small animal models of hemorrhage. Proposed mechanisms for their effect are that they form a mesh analogous to the fibrin plug in native hemostasis and that they may potentiate both platelet activation and the coagulation cascade. These may potentially become valuable adjuncts to endoscopic skull base surgery where there is the potential for both major vessel injury and smaller perforator injury to eloquent areas where bipolar cautery may not be suitable. We present a summary of the clinical studies to date and a small pilot study of nano-hemostat in an endoscopic sheep model of major vessel hemorrhage to determine its efficacy in stopping bleeding in this potentially catastrophic complication.
Keywords: endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery; hemorrhage control; internal carotid artery injury; nano-medicine; pituitary surgery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early and late complications of endoscopic hemostatic techniques following different carotid artery injury characteristics.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014 Aug;4(8):651-7. doi: 10.1002/alr.21326. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014. PMID: 24678066 Clinical Trial.
-
Stress response and communication in surgeons undergoing training in endoscopic management of major vessel hemorrhage: a mixed methods study.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017 Jun;7(6):576-583. doi: 10.1002/alr.21941. Epub 2017 May 8. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017. PMID: 28481016
-
Endoscopic direct vessel closure in carotid artery injury.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Mar;5(3):253-7. doi: 10.1002/alr.21453. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 25504682
-
Management of carotid artery injury in endonasal surgery.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Oct;18(Suppl 2):S173-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1395266. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. PMID: 25992141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine-induced transient hypotension for carotid artery injury during endoscopic skull-base surgery: case report and review of the literature.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019 Sep;9(9):1023-1029. doi: 10.1002/alr.22381. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019. PMID: 31291066 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress Toward the Clinical Translation of Bioinspired Peptide and Protein Assemblies.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Mar;7(5):1700930. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700930. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29115746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellis-Behnke R, Jonas J B. Redefining tissue engineering for nanomedicine in ophthalmology. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011;89(02):e108–e114. - PubMed
-
- Sang L Y, Liang Y X, Li Y et al.A self-assembling nanomaterial reduces acute brain injury and enhances functional recovery in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2015;11(03):611–620. - PubMed
-
- Hirst A R, Escuder B, Miravet J F, Smith D K. High-tech applications of self-assembling supramolecular nanostructured gel-phase materials: from regenerative medicine to electronic devices. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47(42):8002–8018. - PubMed
-
- Loo Y, Zhang S, Hauser C A. From short peptides to nanofibers to macromolecular assemblies in biomedicine. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30(03):593–603. - PubMed
-
- Ellis-Behnke R. At the nanoscale: nanohemostat, a new class of hemostatic agent. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2011;3(01):70–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

