The neuronal and astrocytic protein SLC38A10 transports glutamine, glutamate, and aspartate, suggesting a role in neurotransmission
- PMID: 28593130
- PMCID: PMC5458457
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12219
The neuronal and astrocytic protein SLC38A10 transports glutamine, glutamate, and aspartate, suggesting a role in neurotransmission
Abstract
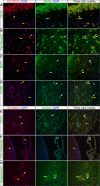
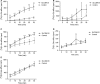
In brain cells, glutamine transporters are vital to monitor and control the levels of glutamate and GABA. There are 11 members of the SLC38 family of amino acid transporters of which eight have been functionally characterized. Here, we report the first histological and functional characterization of the previously orphan member, SLC38A10. We used pairwise global sequence alignments to determine the sequence identity between the SLC38 family members. SLC38A10 was found to share 20-25% transmembrane sequence identity with several family members, and was predicted to have 11 transmembrane helices. SLC38A10 immunostaining was abundant in mouse brain using a custom-made anti-SLC38A10 antibody and colocalization of SLC38A10 immunoreactivity with markers for neurons and astrocytes was detected. Using Xenopus laevis oocytes overexpressing SLC38A10, we show that SLC38A10 mediates bidirectional transport of l-glutamine, l-alanine, l-glutamate, and d-aspartate, and efflux of l-serine. This profile mostly resembles system A members of the SLC38 family. In conclusion, the bidirectional transport of glutamine, glutamate, and aspartate by SLC38A10, and the immunostaining detected in neurons and astrocytes, suggest that SLC38A10 plays a role in pathways involved in neurotransmission.
Keywords: SLC38A10; glutamate/GABA‐glutamine cycle; glutamine transport; immunohistochemistry; solute carriers.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SLC38A10 Regulate Glutamate Homeostasis and Modulate the AKT/TSC2/mTOR Pathway in Mouse Primary Cortex Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 5;10:854397. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.854397. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35450293 Free PMC article.
-
SLC38A10 Transporter Plays a Role in Cell Survival Under Oxidative Stress and Glutamate Toxicity.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 5;8:671865. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671865. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026845 Free PMC article.
-
Transport of L-glutamine, L-alanine, L-arginine and L-histidine by the neuron-specific Slc38a8 (SNAT8) in CNS.J Mol Biol. 2015 Mar 27;427(6 Pt B):1495-1512. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.10.016. Epub 2014 Oct 30. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25451601
-
Roles of glutamine in neurotransmission.Neuron Glia Biol. 2010 Nov;6(4):263-76. doi: 10.1017/S1740925X11000093. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010. PMID: 22018046 Review.
-
Metabolic trafficking between neurons and astrocytes: the glutamate/glutamine cycle revisited.Dev Neurosci. 1995;17(4):203-11. doi: 10.1159/000111288. Dev Neurosci. 1995. PMID: 8575339 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional Stress Induced by Amino Acid Starvation Results in Changes for Slc38 Transporters in Immortalized Hypothalamic Neuronal Cells and Primary Cortex Cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 May 8;5:45. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00045. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29868606 Free PMC article.
-
SLC38A10 Deficiency in Mice Affects Plasma Levels of Threonine and Histidine in Males but Not in Females: A Preliminary Characterization Study of SLC38A10-/- Mice.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;14(4):835. doi: 10.3390/genes14040835. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107593 Free PMC article.
-
SLC38A10 Regulate Glutamate Homeostasis and Modulate the AKT/TSC2/mTOR Pathway in Mouse Primary Cortex Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 5;10:854397. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.854397. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35450293 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer- and behavior-related genes are targeted by selection in the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii).PLoS One. 2018 Aug 13;13(8):e0201838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201838. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30102725 Free PMC article.
-
Role of autophagy in neurotoxic protein's clearance following post-ischemic stroke: where we are and what we know?Mol Brain. 2025 Jul 8;18(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13041-025-01201-1. Mol Brain. 2025. PMID: 40629391 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amara SG and Fontana AC (2002) Excitatory amino acid transporters: keeping up with glutamate. Neurochem Int 41, 313–318. - PubMed
-
- Hediger MA, Romero MF, Peng JB, Rolfs A, Takanaga H and Bruford EA (2004) The ABCs of solute carriers: physiological, pathological and therapeutic implications of human membrane transport proteinsIntroduction. Pflugers Archiv: Europ J Physiol 447, 465–468. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

