DNA-induced unfolding of the thyroid hormone receptor α A/B domain through allostery
- PMID: 28593140
- PMCID: PMC5458466
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12229
DNA-induced unfolding of the thyroid hormone receptor α A/B domain through allostery
Abstract
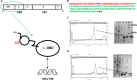
The A/B domains of nuclear receptors such as thyroid receptor α (TRα) are considered to be conformationally flexible and can potentially adopt multiple structural conformations. We used intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence quenching and circular dichroism spectroscopy to characterize the unfolding of this A/B domain upon DNA binding to the contiguous DNA-binding domain (DBD). We propose that this allosteric change in A/B domain conformation can allow it to make the multiple interactions with distinct molecular factors of the transcriptional preinitiation complex. We further suggest that by influencing the affinity of the DBD for DNA, A/B domain can fine-tune the recognition of promotor DNA by TRα.
Keywords: A/B domain; interdomain allostery; intrinsically disordered protein domain; nuclear receptor; protein–DNA interactions; thyroid receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Thompson CC, Weinberger C, Lebo R and Evans RM (1987) Identification of a novel thyroid hormone receptor expressed in the mammalian central nervous system. Science 237, 1610–1614. - PubMed
-
- Lazar MA (1993) Thyroid hormone receptors: multiple forms, multiple possibilities. Endocr Rev 14, 184–193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

