The first identified cathelicidin from tree frogs possesses anti-inflammatory and partial LPS neutralization activities
- PMID: 28593346
- PMCID: PMC5561178
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-017-2449-7
The first identified cathelicidin from tree frogs possesses anti-inflammatory and partial LPS neutralization activities
Abstract
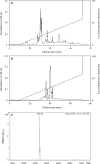
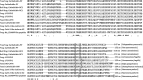
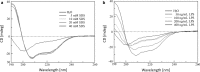
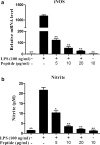
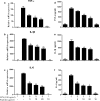
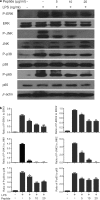
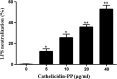
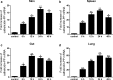
As of February 2017, approximately 7639 amphibian species have been described in the AmphibiaWeb database. However, only 20 cathelicidin-like antimicrobial peptides have been identified to date from 10 amphibian species. Half of these peptides were identified from genome sequences and have not yet been functionally characterized. In this study, a novel cathelicidin-like peptide designated cathelicidin-PP was purified from the skin of tree frog Polypedates puerensis. Cathelicidin-PP is a 32 residue peptide of sequence ASENGKCNLLCLVKKKLRAVGNVIKTVVGKIA. Circular dichroism spectroscopy indicated that cathelicidin-PP mainly adopts a β-sheet structure in membrane-mimetic solutions. Cathelicidin-PP exhibits potent antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi, especially Gram-negative bacteria. Meanwhile, it shows low cytotoxicity toward mammalian cells. Scanning electron microscopy analysis indicated that cathelicidin-PP kills bacteria through the disruption of the bacterial cell membrane integrity. Furthermore, cathelicidin-PP exerts significant anti-inflammatory functions by inhibiting the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated generation of nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6. The MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38) and NF-κB signaling pathways are involved in the anti-inflammatory effect. Cathelicidin-PP caused partial neutralization of LPS in a dose-dependent manner. Quantitative PCR indicated that infection of tree frogs with bacteria causes increased expression of cathelicidin-PP in immune-related tissues. Taken together, cathelicidin-PP is the first identified cathelicidin-like peptide from tree frogs. Our findings demonstrate that in addition to direct bactericidal capacity, cathelicidin-PP also possesses immunomodulatory properties, including partial neutralization of LPS, and inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: Anti-inflammation; Cathelicidin; LPS neutralization; Polypedates puerensis; Tree frog.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure and function of a potent lipopolysaccharide-binding antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory peptide.J Med Chem. 2013 May 9;56(9):3546-56. doi: 10.1021/jm4004158. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23594231
-
As-CATH1-6, novel cathelicidins with potent antimicrobial and immunomodulatory properties from Alligator sinensis, play pivotal roles in host antimicrobial immune responses.Biochem J. 2017 Aug 10;474(16):2861-2885. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170334. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28798159
-
Tree Frog-Derived Cathelicidin Protects Mice against Bacterial Infection through Its Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Regulatory Effect on Phagocytes.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 10;9(11):2252-2268. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00316. Epub 2023 Oct 19. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37855266
-
The Potential of Frog Skin-Derived Peptides for Development into Therapeutically-Valuable Immunomodulatory Agents.Molecules. 2017 Dec 13;22(12):2071. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122071. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29236056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cathelicidin Peptide LL-37, an Antimicrobial Agent, in a Murine Sepsis Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 19;21(17):5973. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175973. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A non-bactericidal cathelicidin provides prophylactic efficacy against bacterial infection by driving phagocyte influx.Elife. 2022 Feb 23;11:e72849. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72849. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35195067 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and functional analysis of cathelicidin-MH, a novel frog-derived peptide with anti-septicemic properties.Elife. 2021 Apr 20;10:e64411. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64411. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33875135 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics resources for the Australian southern stuttering frog (Mixophyes australis) reveal assorted antimicrobial peptides.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 18;14(1):3991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54522-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38368484 Free PMC article.
-
A frog cathelicidin peptide effectively promotes cutaneous wound healing in mice.Biochem J. 2018 Sep 11;475(17):2785-2799. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180286. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30045878 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of two novel cathelicidins from the frog Odorrana livida.Zool Res. 2019 Mar 18;40(2):94-101. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2018.062. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Zool Res. 2019. PMID: 30127328 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

