Antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of Garcinia indica fruit rind via monoaminergic pathway
- PMID: 28593516
- PMCID: PMC5462661
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-017-0766-x
Antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of Garcinia indica fruit rind via monoaminergic pathway
Abstract
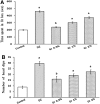
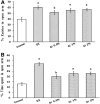
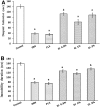
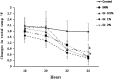
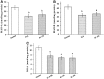
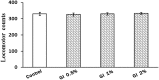
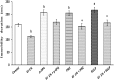
Depression and anxiety are the most crippling neuropsychiatric disorders of this modern era. These mostly occur as anxiety followed by depression or in mixed state. Therefore, there is an urgent need of a safe and effective treatment, which proves its worth in this ailment. What else than a conventional food would be a better choice for a convenient therapy. Therefore, Garcinia indica, commonly known as Kokam, fruit rind has been used in the present study to investigate its antidepressant and anti-anxiety potential using forced swim test, tail suspension test, and reserpine-induced hypothermia; and elevated plus maze, hole-board test, and light dark model, respectively. Garcinia indica fruit rind given to mice with food for consecutive 14 days at 0.5, 1, and 2% w/w significantly (p < 0.05) reduced despair behavior in forced swim test, immobility duration in tail suspension test, and also switched the hypothermia (reserpine induced) to normal temperature significantly (p < 0.05). Garcinia indica significantly (p < 0.05) raised the time elapsed and count of entries in open arms of elevated plus maze, enhanced incidence of head dipping in holes of hole board along with duration of expending time in lit compartment of light dark model, exhibiting its anti-anxiety effect. Garcinia indica significantly reduced monoamine oxidase and malondialdehyde levels providing support to neuroprotective potential of fruit rind. The mechanistic study showed the participation of G. indica at α1-adrenoceptor and D2-dopamine receptor, by attenuating prazosin and sulpiride-induced increase in immobility duration. Garcinia indica fruit rind showed a significant antidepressant and anxiolytic effect while no effect on locomotor activity, i.e., no psycho-stimulation.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Garcinia indica; Malondialdehyde; Monoamine oxidase-A and B; Rind.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arakawa S, Shirayama Y, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Horio M, Muneoka K, Iyo M, Hashimoto K. Minocycline produced antidepressant-like effects on the learned helplessness rats with alterations in levels of monoamine in the amygdala and no changes in BDNF levels in the hippocampus at baseline. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012;100:601–606. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.09.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baliga MS, Bhat HP, Pai RJ, Boloor R, Palatty PL. The chemistry and medicinal uses of the underutilized Indian fruit tree Garcinia indica Choisy (kokum): a review. Food Res Int. 2011;44:1790–1799. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.01.064. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

