Initial anticoagulation in patients with pulmonary embolism: thrombolysis, unfractionated heparin, LMWH, fondaparinux, or DOACs?
- PMID: 28593681
- PMCID: PMC5651323
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13340
Initial anticoagulation in patients with pulmonary embolism: thrombolysis, unfractionated heparin, LMWH, fondaparinux, or DOACs?
Abstract
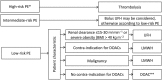
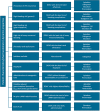
The initial treatment of haemodynamically stable patients with pulmonary embolism (PE) has dramatically changed since the introduction of low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs). With the recent discovery of the direct oral anticoagulant drugs (DOACs), initial treatment of PE will be simplified even further. In several large clinical trials it has been demonstrated that DOACs are not inferior to standard therapy for the initial treatment of PE, and because of their practicability they are becoming the agents of first choice. However, many relative contraindications to DOACs were exclusion criteria in the clinical trials. Therefore, LMWHs will continue to play an important role in initial PE treatment and in some cases there still is a role for unfractionated heparin (UFH). In this review we will give an overview of the biophysical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of anticoagulants currently available for the initial management of PE. In addition, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the indications for the use of UFH, LMWHs and DOACs in the initial management of PE from a pharmacokinetic/-dynamic point of view.
Keywords: DOAC; LMWH; anticoagulation; pulmonary embolism; unfractionated heparin.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute pulmonary embolism. Part 2: treatment.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 Nov;7(11):613-22. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.141. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20842179 Review.
-
Trends in Initial Anticoagulation Among US Patients Hospitalized With Acute Pulmonary Embolism 2011-2020.Ann Emerg Med. 2024 Nov;84(5):518-529. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2024.05.009. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Ann Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38888528
-
[Antithrombotic Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2020 Jul;145(14):970-977. doi: 10.1055/a-0955-3379. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2020. PMID: 32668468 German.
-
Update on pharmacologic therapy for pulmonary embolism.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;19(2):159-69. doi: 10.1177/1074248413506612. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24177334 Review.
-
Current perspectives on the treatment of venous thromboembolism: need for effective, safe and convenient new antithrombotic drugs.Int J Clin Pract. 2004 Mar;58(3):277-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1368-5031.2004.00147.x. Int J Clin Pract. 2004. PMID: 15117096 Review.
Cited by
-
Precautions during Direct Oral Anticoagulant Introduction in Gynecologic Malignancies: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;15(4):1132. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041132. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831475 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary Catheter-Based Treatment Options for Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2021;23(7):44. doi: 10.1007/s11936-021-00920-7. Epub 2021 May 12. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33994774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Therapeutic Response to Unfractionated Heparin Therapy: Machine Learning Approach.Interact J Med Res. 2022 Sep 19;11(2):e34533. doi: 10.2196/34533. Interact J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35993617 Free PMC article.
-
Anticoagulation reversal (vitamin K, prothrombin complex concentrates, idarucizumab, andexanet-α, protamine).Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;91(3):604-614. doi: 10.1111/bcp.16142. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 38926082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How enoxaparin underdosing and sex contribute to achieving therapeutic anti-Xa levels.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 12;15:1377232. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1377232. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39070792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barritt DW, Jordan SC. Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism: a controlled trial. Lancet 1960; 1: 1309–1312. - PubMed
-
- Kernohan RJ, Todd C. Heparin therapy in thromboembolic disease. Lancet 1966; 1: 621–623. - PubMed
-
- Kanis JA. Heparin in the treatment of pulmonary thromboembolism. Thromb Diath Haemorrh 1974; 32: 519–527. - PubMed
-
- Alpert JS, Smith R, Carlson J, Ockene IS, Dexter L, Dalen JE. Mortality in patients treated for pulmonary embolism. JAMA 1976; 236: 1477–1480. - PubMed
-
- Brandjes DP, Heijboer H, Buller HR, de Rijk M, Jagt H, ten Cate JW. Acenocoumarol and heparin compared with acenocoumarol alone in the initial treatment of proximal‐vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med 1992; 327: 1485–1489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

