Osmoregulated Periplasmic Glucans
- PMID: 28593831
- PMCID: PMC11575687
- DOI: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0001-2017
Osmoregulated Periplasmic Glucans
Abstract
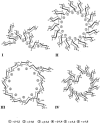
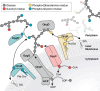
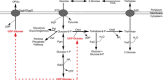
Among all the systems developed by enterobacteria to face osmotic stress, only osmoregulated periplasmic glucans (OPGs) were found to be modulated during osmotic fluxes. First detected in 1973 by E.P. Kennedy's group in a study of phospholipid turnover in Escherichia coli, OPGs have been shown across alpha, beta, and gamma subdivisions of the proteobacteria. Discovery of OPG-like compounds in the epsilon subdivision strongly suggested that the presence of periplasmic glucans is essential for almost all proteobacteria. This article offers an overview of the different classes of OPGs. Then, the biosynthesis of OPGs and their regulation in E. coli and other species are discussed. Finally, the biological role of OPGs is developed. Beyond structural function, OPGs are involved in pathogenicity, in particular, by playing a role in signal transduction pathways. Recently, OPG synthesis proteins have been suggested to control cell division and growth rate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New insights into the biological role of the osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in pathogenic and symbiotic bacteria.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015 Oct;7(5):690-7. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12325. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26265506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concentration of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans (OPGs) modulates the activation level of the RcsCD RcsB phosphorelay in the phytopathogen bacteria Dickeya dadantii.Environ Microbiol. 2013 Mar;15(3):881-94. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12054. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23253096
-
Osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in Proteobacteria.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 May 1;186(1):11-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09075.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 10779706 Review.
-
Osmoregulated periplasmic glucan polymerization requires constant protein synthesis in Escherichia coli.Curr Microbiol. 2010 Nov;61(5):396-400. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9625-2. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Curr Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20358372
-
The virulence of a Dickeya dadantii 3937 mutant devoid of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans is restored by inactivation of the RcsCD-RcsB phosphorelay.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jul;192(13):3484-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.00143-10. Epub 2010 Apr 23. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20418397 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Anomer-Inverting Transglycosylase: Cyclic Glucohexadecaose-Producing Enzyme from Xanthomonas, a Phytopathogen.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Jul 3;146(26):17738-17746. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c02579. Epub 2024 Jun 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38957137 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of genes involved in efflux function and regulation within Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Feb;169(2):001296. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001296. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 36745554 Free PMC article.
-
The Rcs System Contributes to the Motility Defects of the Twin-Arginine Translocation System Mutant of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2022 Apr 19;204(4):e0061221. doi: 10.1128/jb.00612-21. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35311558 Free PMC article.
-
The Klebsiella pneumoniae ter Operon Enhances Stress Tolerance.Infect Immun. 2023 Feb 16;91(2):e0055922. doi: 10.1128/iai.00559-22. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 36651775 Free PMC article.
-
Tazobactam selects for multidrug resistance.NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2025 May 30;3(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s44259-025-00122-2. NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2025. PMID: 40447858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman PL. 1961. Physical properties and chemical composition of urine: mammals, p 363–369. In Dittmer DS (ed), Blood and Other Bodily Fluids. Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Washington, DC.
-
- Kunin CM. 1987. Detection, Prevention and Management of Urinary Tract Infections, 4th ed. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Ross DL, Neely AE. 1983. Textbook of Urinalysis and Bodily Fluids. Appleton Century Crofts, Norwalk, VA.
-
- Russell PJ, Hertz PE, McMillan B. 2017. Regulating the internal environment, p 1041, Biology: The Dynamic Science, 4th ed. Brooks Cole, Salt Lake City, UT.
-
- Purves WK, Sadava D, Orians GH, Heller C. 2003. Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion, Life: The Science of Biology, 7th ed. Sinauer Associates and W. H. Freeman, Sunderland, MA.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

