Protein-directed ribosomal frameshifting temporally regulates gene expression
- PMID: 28593994
- PMCID: PMC5472766
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15582
Protein-directed ribosomal frameshifting temporally regulates gene expression
Abstract
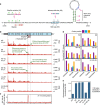
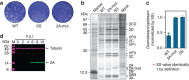
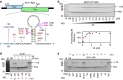
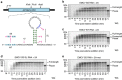
Programmed -1 ribosomal frameshifting is a mechanism of gene expression, whereby specific signals within messenger RNAs direct a proportion of translating ribosomes to shift -1 nt and continue translating in the new reading frame. Such frameshifting normally occurs at a set ratio and is utilized in the expression of many viral genes and a number of cellular genes. An open question is whether proteins might function as trans-acting switches to turn frameshifting on or off in response to cellular conditions. Here we show that frameshifting in a model RNA virus, encephalomyocarditis virus, is trans-activated by viral protein 2A. As a result, the frameshifting efficiency increases from 0 to 70% (one of the highest known in a mammalian system) over the course of infection, temporally regulating the expression levels of the viral structural and enzymatic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An analysis by metabolic labelling of the encephalomyocarditis virus ribosomal frameshifting efficiency and stimulators.J Gen Virol. 2017 Aug;98(8):2100-2105. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000888. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Gen Virol. 2017. PMID: 28786807 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the stimulators of protein-directed ribosomal frameshifting in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 5;47(15):8207-8223. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz503. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31180502 Free PMC article.
-
A sequence required for -1 ribosomal frameshifting located four kilobases downstream of the frameshift site.J Mol Biol. 2001 Jul 27;310(5):987-99. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4801. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11502008
-
Changed in translation: mRNA recoding by -1 programmed ribosomal frameshifting.Trends Biochem Sci. 2015 May;40(5):265-74. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015. PMID: 25850333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal frameshifting and transcriptional slippage: From genetic steganography and cryptography to adventitious use.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7007-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw530. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27436286 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A frameshift in time.Elife. 2022 Apr 11;11:e78373. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78373. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35404784 Free PMC article.
-
The energy landscape of -1 ribosomal frameshifting.Sci Adv. 2020 Jan 1;6(1):eaax6969. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6969. eCollection 2020 Jan. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 31911945 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of HIV-1 Gag-Pol Expression by Shiftless, an Inhibitor of Programmed -1 Ribosomal Frameshifting.Cell. 2019 Jan 24;176(3):625-635.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.030. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30682371 Free PMC article.
-
Codon usage bias.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):539-565. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06749-4. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34822069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streamlined and sensitive mono- and di-ribosome profiling in yeast and human cells.Nat Methods. 2023 Nov;20(11):1704-1715. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-02028-1. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Nat Methods. 2023. PMID: 37783882 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

