Synthesis and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of [R₄W₄K]-Levofloxacin and [R₄W₄K]-Levofloxacin-Q Conjugates
- PMID: 28594345
- PMCID: PMC6152667
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22060957
Synthesis and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of [R₄W₄K]-Levofloxacin and [R₄W₄K]-Levofloxacin-Q Conjugates
Abstract
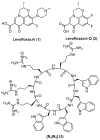
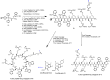
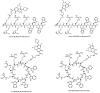
The development of a new class of antibiotics to fight bacterial resistance is a time-consuming effort associated with high-cost and commercial risks. Thus, modification, conjugation or combination of existing antibiotics to enhance their efficacy is a suitable strategy. We have previously reported that the amphiphilic cyclic peptide [R₄W₄] had antibacterial activity with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 2.97 µg/mL against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Herein, we hypothesized that conjugation or combination of the amphiphilic cyclic peptide [R₄W₄] with levofloxacin or levofloxacin-Q could improve the antibacterial activity of levofloxacin and levofloxacin-Q. Fmoc/tBu solid-phase chemistry was employed to synthesize conjugates of [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin-Q and [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin. The carboxylic acid group of levofloxacin or levofloxacin-Q was conjugated with the amino group of β-alanine attached to lysine in the presence of 2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HBTU) and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) for 3 h to afford the products. Antibacterial assays were conducted to determine the potency of conjugates [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin-Q and [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin against MRSA and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Although levofloxacin-Q was inactive even at a concentration of 128 µg/mL, [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin-Q conjugate and the corresponding physical mixture showed MIC values of 8 µg/mL and 32 µg/mL against MRSA and Klebsiella pneumonia, respectively, possibly due to the activity of the peptide. On the other hand, [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin conjugate (MIC = 32 µg/mL and MIC = 128 µg/mL) and the physical mixture (MIC = 8 µg/mL and 32 µg/mL) was less active than levofloxacin (MIC = 2 µg/mL and 4 = µg/mL) against MRSA and Klebsiella pneumoniae, respectively. The data showed that the conjugation of levofloxacin with [R₄W₄K] significantly reduced the antibacterial activity compared to the parent analogs, while [R₄W₄K]-levofloxacin-Q conjugate was more significantly potent than levofloxacin-Q alone.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumonia; amphiphilic cyclic peptide; combination; conjugation; levofloxacin; levofloxacin-Q; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

