DHRS9 Is a Stable Marker of Human Regulatory Macrophages
- PMID: 28594751
- PMCID: PMC6319563
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001814
DHRS9 Is a Stable Marker of Human Regulatory Macrophages
Abstract
Background: The human regulatory macrophage (Mreg) has emerged as a promising cell type for use as a cell-based adjunct immunosuppressive therapy in solid organ transplant recipients. In this brief report, dehydrogenase/reductase 9 (DHRS9) is identified as a robust marker of human Mregs.
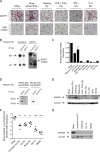
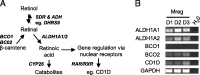
Methods: The cognate antigen of a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against human Mregs was identified as DHRS9 by immunoprecipitation and MALDI-MS sequencing. Expression of DHRS9 within a panel of monocyte-derived macrophages was investigated by quantitative PCR, immunoblotting and flow cytometry.
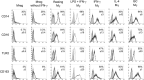
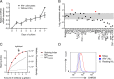
Results: DHRS9 expression discriminated human Mregs from a panel of in vitro derived macrophages in other polarisation states. Likewise, DHRS9 expression distinguished Mregs from a variety of human monocyte-derived tolerogenic antigen-presenting cells in current development as cell-based immunotherapies, including Tol-DC, Rapa-DC, DC-10, and PGE2-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells. A subpopulation of DHRS9-expressing human splenic macrophages was identified by immunohistochemistry. Expression of DHRS9 was acquired gradually during in vitro development of human Mregs from CD14 monocytes and was further enhanced by IFN-γ treatment on day 6 of culture. Stimulating Mregs with 100 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide for 24 hours did not extinguish DHRS9 expression. Dhrs9 was not an informative marker of mouse Mregs.
Conclusion: DHRS9 is a specific and stable marker of human Mregs.
Conflict of interest statement
J.A.H. and E.K.G. are the named inventors on European Patent Office (EPO) filing 16159985.6-1402 dated 11.03.2016, “Immunoregulatory cells and methods for their production.” All other authors declare no conflict-of-interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
A New Marker for Regulatory Macrophages.Transplantation. 2017 Nov;101(11):2659-2660. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001863. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 28650423 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hutchinson JA, Geissler EK. Now or never? The case for cell-based immunosuppression in kidney transplantation. Kidney Int. 2015;87:1116–1124. - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson JA, Riquelme P, Geissler EK, et al. Human regulatory macrophages. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;677:181–192. - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson JA, Riquelme P, Sawitzki B, et al. Cutting edge: immunological consequences and trafficking of human regulatory macrophages administered to renal transplant recipients. J Immunol. 2011;187:2072–2078. - PubMed
-
- Ahrens N, Riquelme P, Bach C, et al. Donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies present in pooled human serum do not prevent development of human Mreg_UKR from monocytes in culture. Transplantation. 2017;101:e188–e190. - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson JA. Macrophages in transplantation. Transplantation. 2015;99:898–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

